Specialized interferon action in COVID-19
- PMID: 35217532
- PMCID: PMC8931386
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2116730119
Specialized interferon action in COVID-19
Abstract
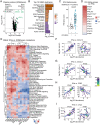
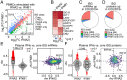
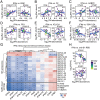
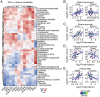
The impacts of interferon (IFN) signaling on COVID-19 pathology are multiple, with both protective and harmful effects being documented. We report here a multiomics investigation of systemic IFN signaling in hospitalized COVID-19 patients, defining the multiomics biosignatures associated with varying levels of 12 different type I, II, and III IFNs. The antiviral transcriptional response in circulating immune cells is strongly associated with a specific subset of IFNs, most prominently IFNA2 and IFNG. In contrast, proteomics signatures indicative of endothelial damage and platelet activation associate with high levels of IFNB1 and IFNA6. Seroconversion and time since hospitalization associate with a significant decrease in a specific subset of IFNs. Additionally, differential IFN subtype production is linked to distinct constellations of circulating myeloid and lymphoid immune cell types. Each IFN has a unique metabolic signature, with IFNG being the most associated with activation of the kynurenine pathway. IFNs also show differential relationships with clinical markers of poor prognosis and disease severity. For example, whereas IFNG has the strongest association with C-reactive protein and other immune markers of poor prognosis, IFNB1 associates with increased neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio, a marker of late severe disease. Altogether, these results reveal specialized IFN action in COVID-19, with potential diagnostic and therapeutic implications.
Keywords: COVID-19; CyTOF; SARS-CoV-2; cytokine; interferon.
Copyright © 2022 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interest statement: J.M.E. serves on the COVID Development Advisory Board for Eli Lilly.
Figures



References
-
- Galani I. E., et al. , Untuned antiviral immunity in COVID-19 revealed by temporal type I/III interferon patterns and flu comparison. Nat. Immunol. 22, 32–40 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Bastard P., et al. ; HGID Lab; NIAID-USUHS Immune Response to COVID Group; COVID Clinicians; COVID-STORM Clinicians; Imagine COVID Group; French COVID Cohort Study Group; Milieu Intérieur Consortium; CoV-Contact Cohort; Amsterdam UMC Covid-19 Biobank; COVID Human Genetic Effort, Autoantibodies against type I IFNs in patients with life-threatening COVID-19. Science 370, eabd4585 (2020). - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL146442/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RM1 GM131968/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK048520/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI150305/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002535/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI145988/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI134220/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K23 AR070897/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM124939/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL148151/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 HL150032/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL149714/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI172546/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA046934/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

