Structure-guided engineering of tick evasins for targeting chemokines in inflammatory diseases
- PMID: 35217625
- PMCID: PMC8892493
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2122105119
Structure-guided engineering of tick evasins for targeting chemokines in inflammatory diseases
Abstract
As natural chemokine inhibitors, evasin proteins produced in tick saliva are potential therapeutic agents for numerous inflammatory diseases. Engineering evasins to block the desired chemokines and avoid off-target side effects requires structural understanding of their target selectivity. Structures of the class A evasin EVA-P974 bound to human CC chemokine ligands 7 and 17 (CCL7 and CCL17) and to a CCL8-CCL7 chimera reveal that the specificity of class A evasins for chemokines of the CC subfamily is defined by conserved, rigid backbone-backbone interactions, whereas the preference for a subset of CC chemokines is controlled by side-chain interactions at four hotspots in flexible structural elements. Hotspot mutations alter target preference, enabling inhibition of selected chemokines. The structure of an engineered EVA-P974 bound to CCL2 reveals an underlying molecular mechanism of EVA-P974 target preference. These results provide a structure-based framework for engineering evasins as targeted antiinflammatory therapeutics.
Keywords: chemokines; inflammatory diseases; protein engineering; tick evasins.
Copyright © 2022 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
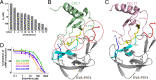

References
-
- Zlotnik A., Yoshie O., Chemokines: A new classification system and their role in immunity. Immunity 12, 121–127 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Moore J. P., et al. , M2 macrophage accumulation in the aortic wall during angiotensin II infusion in mice is associated with fibrosis, elastin loss, and elevated blood pressure. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 309, H906–H917 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Zhao S., Wu B., Stevens R. C., Advancing chemokine GPCR structure based drug discovery. Structure 27, 405–408 (2019). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

