CSB-independent, XPC-dependent transcription-coupled repair in Drosophila
- PMID: 35217627
- PMCID: PMC8892495
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2123163119
CSB-independent, XPC-dependent transcription-coupled repair in Drosophila
Abstract
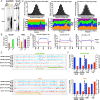
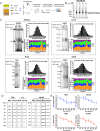
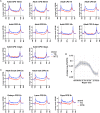
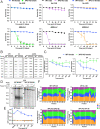
Drosophila melanogaster has been extensively used as a model system to study ionizing radiation and chemical-induced mutagenesis, double-strand break repair, and recombination. However, there are only limited studies on nucleotide excision repair in this important model organism. An early study reported that Drosophila lacks the transcription-coupled repair (TCR) form of nucleotide excision repair. This conclusion was seemingly supported by the Drosophila genome sequencing project, which revealed that Drosophila lacks a homolog to CSB, which is known to be required for TCR in mammals and yeasts. However, by using excision repair sequencing (XR-seq) genome-wide repair mapping technology, we recently found that the Drosophila S2 cell line performs TCR comparable to human cells. Here, we have extended this work to Drosophila at all its developmental stages. We find TCR takes place throughout the life cycle of the organism. Moreover, we find that in contrast to humans and other multicellular organisms previously studied, the XPC repair factor is required for both global and transcription-coupled repair in Drosophila.
Keywords: XPC; XR-seq; transcription-coupled repair.
Copyright © 2022 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nucleotide excision repair in Human cell lines lacking both XPC and CSB proteins.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Jul 7;51(12):6238-6245. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad334. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 37144462 Free PMC article.
-
Stress-induced Cdk5 activity enhances cytoprotective basal autophagy in Drosophila melanogaster by phosphorylating acinus at serine437.Elife. 2017 Dec 11;6:e30760. doi: 10.7554/eLife.30760. Elife. 2017. PMID: 29227247 Free PMC article.
-
Antidepressants for pain management in adults with chronic pain: a network meta-analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Oct;28(62):1-155. doi: 10.3310/MKRT2948. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39367772 Free PMC article.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
Cited by
-
Dynamics of transcription-coupled repair of cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers and (6-4) photoproducts in Escherichia coli.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Oct 29;121(44):e2416877121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2416877121. Epub 2024 Oct 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 39441633 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide analysis of transcription-coupled repair reveals novel transcription events in Caenorhabditis elegans.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Mar 29:2023.10.12.562083. doi: 10.1101/2023.10.12.562083. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: PLoS Genet. 2024 Jul 19;20(7):e1011365. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1011365. PMID: 37904932 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Evolutionary Insights into the Length Variation of DNA Damage Response Proteins Across Eukaryotes.Genome Biol Evol. 2025 May 30;17(6):evaf089. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evaf089. Genome Biol Evol. 2025. PMID: 40388363 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide analysis of transcription-coupled repair reveals novel transcription events in Caenorhabditis elegans.PLoS Genet. 2024 Jul 19;20(7):e1011365. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1011365. eCollection 2024 Jul. PLoS Genet. 2024. PMID: 39028758 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-species investigation into the requirement of XPA for nucleotide excision repair.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Jan 25;52(2):677-689. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad1104. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 37994737 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

