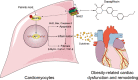
Direct cardio-protection of Dapagliflozin against obesity-related cardiomyopathy via NHE1/MAPK signaling
- PMID: 35217813
- PMCID: PMC9525284
- DOI: 10.1038/s41401-022-00885-8
Direct cardio-protection of Dapagliflozin against obesity-related cardiomyopathy via NHE1/MAPK signaling
Abstract
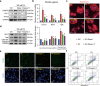
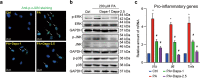
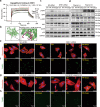
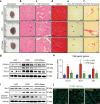
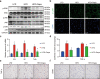
Obesity is an important independent risk factor for cardiovascular diseases, remaining an important health concern worldwide. Evidence shows that saturated fatty acid-induced inflammation in cardiomyocytes contributes to obesity-related cardiomyopathy. Dapagliflozin (Dapa), a selective SGLT2 inhibitor, exerts a favorable preventive activity in heart failure. In this study, we investigated the protective effect of Dapa against cardiomyopathy caused by high fat diet-induced obesity in vitro and in vivo. Cultured rat cardiomyocyte H9c2 cells were pretreated with Dapa (1, 2.5 μM) for 1.5 h, followed by treatment with palmitic acid (PA, 200 μM) for 24 h. We showed that Dapa pretreatment concentration-dependently attenuated PA-induced cell hypertrophy, fibrosis and apoptosis. Transcriptome analysis revealed that inhibition of PA-activated MAPK/AP-1 pathway contributed to the protective effect of Dapa in H9c2 cells, and this was confirmed by anti-p-cJUN fluorescence staining assay. Using surface plasmon resonance analysis we found the direct binding of Dapa with NHE1. Gain and loss of function experiments further demonstrated the role of NHE1 in the protection of Dapa. In vivo experiments were conducted in mice fed a high fat diet for 5 months. The mice were administered Dapa (1 mg·kg-1·d-1, i.g.) in the last 2 months. Dapa administration significantly reduced the body weight and improved the serum lipid profiles. Dapa administration also alleviated HFD-induced cardiac dysfunction and cardiac aberrant remodeling via inhibiting MAPK/AP-1 pathway and ameliorating cardiac inflammation. In conclusion, Dapa exerts a direct protective effect against saturated fatty acid-induced cardiomyocyte injury in addition to the lowering effect on serum lipids. The protective effect results from negative regulating MAPK/AP-1 pathway in a NHE1-dependent way. The current study highlights the potential of clinical use of Dapa in the prevention of obesity-related cardiac dysfunction.
Keywords: Dapagliflozin; MAPK pathway; NHE1; cardiomyopathy; inflammation; obesity; palmitic acid; rat cardiomyocyte H9c2 cell line.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Sciences and Chinese Pharmacological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Schaeffler A, Gross P, Buettner R, Bollheimer C, Buechler C, Neumeier M, et al. Fatty acid-induced induction of Toll-like receptor-4/nuclear factor-kappaB pathway in adipocytes links nutritional signalling with innate immunity. Immunology. 2009;126:233–45. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2008.02892.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

