The m6A reader IGF2BP3 promotes acute myeloid leukemia progression by enhancing RCC2 stability
- PMID: 35217832
- PMCID: PMC8894383
- DOI: 10.1038/s12276-022-00735-x
The m6A reader IGF2BP3 promotes acute myeloid leukemia progression by enhancing RCC2 stability
Abstract
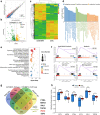
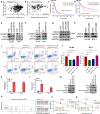
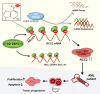
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is the most abundant posttranscriptional modification of mRNA in eukaryotes. Recent evidence suggests that dysregulated m6A-associated proteins and m6A modifications play a pivotal role in the initiation and progression of diseases such as cancer. Here, we identified that IGF2BP3 is specifically overexpressed in acute myeloid leukemia (AML), a subtype of leukemia associated with poor prognosis and high genetic risk. IGF2BP3 is required for maintaining AML cell survival in an m6A-dependent manner, and knockdown of IGF2BP3 dramatically suppresses the apoptosis, reduces the proliferation, and impairs the leukemic capacity of AML cells in vitro and in vivo. Mechanistically, IGF2BP3 interacts with RCC2 mRNA and stabilizes the expression of m6A-modified RNA. Thus, we provided compelling evidence demonstrating that the m6A reader IGF2BP3 contributes to tumorigenesis and poor prognosis in AML and can serve as a target for the development of cancer therapeutics.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
N6-methyladenosine-modified SENP1, identified by IGF2BP3, is a novel molecular marker in acute myeloid leukemia and aggravates progression by activating AKT signal via de-SUMOylating HDAC2.Mol Cancer. 2024 May 31;23(1):116. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-02013-y. Mol Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38822351 Free PMC article.
-
RNA N6-methyladenosine reader IGF2BP3 promotes acute myeloid leukemia progression by controlling stabilization of EPOR mRNA.PeerJ. 2023 Aug 30;11:e15706. doi: 10.7717/peerj.15706. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 37663284 Free PMC article.
-
The m6A reader IGF2BP3 promotes HCC progression by enhancing MCM10 stability.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 10;15(1):8204. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-93062-w. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40065065 Free PMC article.
-
The N6-methyladenosine RNA modification in acute myeloid leukemia.Curr Opin Hematol. 2021 Mar 1;28(2):80-85. doi: 10.1097/MOH.0000000000000636. Curr Opin Hematol. 2021. PMID: 33337619 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functions of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) RNA modifications in acute myeloid leukemia.J Leukoc Biol. 2024 Oct 1;116(4):662-671. doi: 10.1093/jleuko/qiae106. J Leukoc Biol. 2024. PMID: 38721720 Review.
Cited by
-
Epigenetic targeting of autophagy for cancer: DNA and RNA methylation.Front Oncol. 2023 Dec 8;13:1290330. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1290330. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 38148841 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IGF2BPs as novel m6A readers: Diverse roles in regulating cancer cell biological functions, hypoxia adaptation, metabolism, and immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment.Genes Dis. 2023 Jul 20;11(2):890-920. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2023.06.017. eCollection 2024 Mar. Genes Dis. 2023. PMID: 37692485 Free PMC article. Review.
-
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) RNA modification in chronic myeloid leukemia: unveiling a novel therapeutic target.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024 Jul 31;81(1):326. doi: 10.1007/s00018-024-05379-w. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 39085650 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RAB39B: A novel biomarker for acute myeloid leukemia identified via multi-omics and functional validation.Open Med (Wars). 2025 Mar 28;20(1):20251168. doi: 10.1515/med-2025-1168. eCollection 2025. Open Med (Wars). 2025. PMID: 40177653 Free PMC article.
-
DNA methylation in monozygotic twins discordant for acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a case report and systematic review.Clin Epigenetics. 2025 Jun 6;17(1):94. doi: 10.1186/s13148-025-01906-z. Clin Epigenetics. 2025. PMID: 40481591 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Westermann, J. and Bullinger, L. Precision medicine in myeloid malignancies. Semin. Cancer Biol. 10.1016/j.semcancer.2021.03.034 (2021). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

