Oxidative stress-induced endothelial dysfunction and decreased vascular nitric oxide in COVID-19 patients
- PMID: 35219085
- PMCID: PMC8865837
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.103893
Oxidative stress-induced endothelial dysfunction and decreased vascular nitric oxide in COVID-19 patients
Abstract
Background: SARS-CoV-2 targets endothelial cells through the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 receptor. The resulting endothelial injury induces widespread thrombosis and microangiopathy. Nevertheless, early specific markers of endothelial dysfunction and vascular redox status in COVID-19 patients are currently missing.
Methods: Observational study including ICU and non-ICU adult COVID-19 patients admitted in hospital for acute respiratory failure, compared with control subjects matched for cardiovascular risk factors similar to ICU COVID-19 patients, and ICU septic shock patients unrelated to COVID-19.
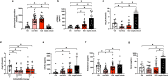
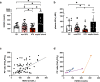
Findings: Early SARS-CoV-2 infection was associated with an imbalance between an exacerbated oxidative stress (plasma peroxides levels in ICU patients vs. controls: 1456.0 ± 400.2 vs 436 ± 272.1 mmol/L; P < 0.05) and a reduced nitric oxide bioavailability proportional to disease severity (5-α-nitrosyl-hemoglobin, HbNO in ICU patients vs. controls: 116.1 ± 62.1 vs. 163.3 ± 46.7 nmol/L; P < 0.05). HbNO levels correlated with oxygenation parameters (PaO2/FiO2 ratio) in COVID-19 patients (R2 = 0.13; P < 0.05). Plasma levels of angiotensin II, aldosterone, renin or serum level of TREM-1 ruled out any hyper-activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system or leucocyte respiratory burst in ICU COVID-19 patients, contrary to septic patients.
Interpretation: Endothelial oxidative stress with ensuing decreased NO bioavailability appears as a likely pathogenic factor of endothelial dysfunction in ICU COVID-19 patients. A correlation between NO bioavailability and oxygenation parameters is observed in hospitalized COVID-19 patients. These results highlight an urgent need for oriented research leading to a better understanding of the specific endothelial oxidative stress that occurs during SARS-CoV-2.
Funding: Stated in the acknowledgments section.
Keywords: Angiotensin II; Endothelial dysfunction; Microvascular thrombosis; Nitric oxide; Oxidative stress; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests Marc Derive is a co-founder and employee of Inotrem Company, a drug development company that is developing anti-TREM-1 approaches in septic shock and COVID-19. The other authors have disclosed that they do not have any potential conflicts of interest.
Figures



Comment in
-
Nitric oxide in COVID-19: Too little of a good thing?EBioMedicine. 2022 Mar;77:103925. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.103925. Epub 2022 Mar 9. EBioMedicine. 2022. PMID: 35278744 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

