Electrocardiographic findings in young competitive athletes during acute SARS-CoV-2 infection
- PMID: 35219112
- PMCID: PMC8858006
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jelectrocard.2022.02.005
Electrocardiographic findings in young competitive athletes during acute SARS-CoV-2 infection
Abstract
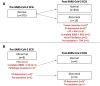
Initial guidelines recommended a 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG) in young competitive athletes following SARS-CoV-2 infection to screen for myocarditis. However, no data are available that detail ECG findings before and after SARS-CoV-2 infection in young athletes without clinical or imaging evidence of overt myocarditis. This study applied the International Criteria for ECG interpretation in a cohort of 378 collegiate athletes to compare ECG findings at baseline and during the acute phase of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Our results suggest that ECG changes can occur in the absence of definitive SARS-CoV-2 cardiac involvement in young competitive athletes.
Keywords: Athlete; Exercise; Myocarditis; SARS-CoV-2; Sudden cardiac arrest.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Comment in
-
Triad and true? Examining the role of the ECG in evaluating young athletes with COVID-19.J Electrocardiol. 2022 May-Jun;72:56-57. doi: 10.1016/j.jelectrocard.2022.02.011. Epub 2022 Mar 12. J Electrocardiol. 2022. PMID: 35313211 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Kim J.H., Levine B.D., Phelan D., Emery M.S., Martinez M.W., Chung E.H., et al. Coronavirus disease 2019 and the athletic heart: emerging perspectives on pathology, risks, and return to play. JAMA Cardiol. 2021;6(2):219–227. - PubMed
-
- Daniels C.J., Rajpal S., Greenshields J.T., Rosenthal G.L., Chung E.H., Terrin M., et al. Prevalence of clinical and subclinical myocarditis in competitive athletes with recent SARS-CoV-2 infection: results from the big ten COVID-19 cardiac registry. JAMA Cardiol. 2021;6(9):1078–1087. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Drezner J.A., Sharma S., Baggish A., Papadakis M., Wilson M.G., Prutkin J.M., et al. International criteria for electrocardiographic interpretation in athletes: consensus statement. Br J Sports Med. 2017;51(9):704–731. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

