A conditional GABAergic synaptic vesicle marker for Drosophila
- PMID: 35219770
- PMCID: PMC8940707
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2022.109540
A conditional GABAergic synaptic vesicle marker for Drosophila
Abstract
Background: Throughout the animal kingdom, GABA is the principal inhibitory neurotransmitter of the nervous system. It is essential for maintaining the homeostatic balance between excitation and inhibition required for the brain to operate normally. Identification of GABAergic neurons and their GABA release sites are thus essential for understanding how the brain regulates the excitability of neurons and the activity of neural circuits responsible for numerous aspects of brain function including information processing, locomotion, learning, memory, and synaptic plasticity, among others.
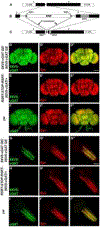
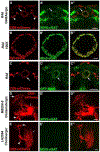
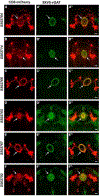
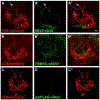
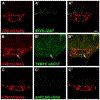
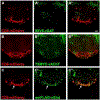
New method: Since the structure and features of GABA synapses are critical to understanding their function within specific neural circuits of interest, here we developed and characterized a conditional marker of GABAergic synaptic vesicles for Drosophila, 9XV5-vGAT.
Results: 9XV5-vGAT is validated for conditionality of expression, specificity for localization to synaptic vesicles, specificity for expression in GABAergic neurons, and functionality. Its utility for GABAergic neurotransmitter phenotyping and identification of GABA release sites was verified for ellipsoid body neurons of the central complex. In combination with previously reported conditional SV markers for acetylcholine and glutamate, 9XV5-vGAT was used to demonstrate fast neurotransmitter phenotyping of subesophageal ganglion neurons.
Comparison with existing methods: This method is an alternative to single cell transcriptomics for neurotransmitter phenotyping and can be applied to any neurons of interest represented by a binary transcription system driver.
Conclusion: A conditional GABAergic synaptic vesicle marker has been developed and validated for GABA neurotransmitter phenotyping and subcellular localization of GABAergic synaptic vesicles.
Keywords: Drosophila; Epitope tag; GABAergic; Synaptic vesicle; VGAT.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
A conditional glutamatergic synaptic vesicle marker for Drosophila.G3 (Bethesda). 2022 Mar 4;12(3):jkab453. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkab453. G3 (Bethesda). 2022. PMID: 35100385 Free PMC article.
-
Unique pH dynamics in GABAergic synaptic vesicles illuminates the mechanism and kinetics of GABA loading.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Sep 20;113(38):10702-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1604527113. Epub 2016 Sep 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27601664 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic and vesicular coexistence of VGLUT and VGAT in selected excitatory and inhibitory synapses.J Neurosci. 2010 Jun 2;30(22):7634-45. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0141-10.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20519538 Free PMC article.
-
Activity-dependent regulation of vesicular glutamate and GABA transporters: a means to scale quantal size.Neurochem Int. 2006 May-Jun;48(6-7):643-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2005.12.029. Epub 2006 Mar 20. Neurochem Int. 2006. PMID: 16546297 Review.
-
Presynaptic control of inhibitory neurotransmitter content in VIAAT containing synaptic vesicles.Neurochem Int. 2016 Sep;98:94-102. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2016.06.002. Epub 2016 Jun 11. Neurochem Int. 2016. PMID: 27296116 Review.
Cited by
-
A conditional strategy for cell-type-specific labeling of endogenous excitatory synapses in Drosophila.Cell Rep Methods. 2023 May 11;3(5):100477. doi: 10.1016/j.crmeth.2023.100477. eCollection 2023 May 22. Cell Rep Methods. 2023. PMID: 37323572 Free PMC article.
-
Two classes of amine/glutamate multi-transmitter neurons innervate Drosophila internal male reproductive organs.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jul 28:2025.07.23.666348. doi: 10.1101/2025.07.23.666348. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40766443 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Rescue of Epilepsy-Associated Mutations of the Highly Conserved Glycine Residue 443 in the Human GABA Transporter 1.FASEB J. 2025 Jun 15;39(11):e70614. doi: 10.1096/fj.202403159RR. FASEB J. 2025. PMID: 40485335 Free PMC article.
-
SynLight: a dicistronic strategy for simultaneous active zone and cell labeling in the Drosophila nervous system.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Jul 17:2023.07.17.549367. doi: 10.1101/2023.07.17.549367. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: G3 (Bethesda). 2023 Nov 1;13(11):jkad221. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkad221. PMID: 37502901 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Horizontal-cell like Dm9 neurons in Drosophila modulate photoreceptor output to supply multiple functions in early visual processing.Front Mol Neurosci. 2024 May 15;17:1347540. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2024.1347540. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38813436 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams MD, Celniker SE, Holt RA, Evans CA, Gocayne JD et al., 2000. The genome sequence of Drosophila melanogaster. Science 287: 2185–2195. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Ari Y, and Holmes GL, 2005. The multiple facets of gamma-aminobutyric acid dysfunction in epilepsy. Curr Opin Neurol 18: 141–145. - PubMed
-
- Certel SJ, and Thor S, 2004. Specification of Drosophila motoneuron identity by the combinatorial action of POU and LIM-HD factors. Development 131: 5429–5439. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

