Trajectory of SARS-CoV-2 anti-S IgG levels following transfusion and a third dose of BNT162b2 vaccine in a patient with massive postoperative bleeding: A case report
- PMID: 35219885
- PMCID: PMC8866168
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijid.2022.02.042
Trajectory of SARS-CoV-2 anti-S IgG levels following transfusion and a third dose of BNT162b2 vaccine in a patient with massive postoperative bleeding: A case report
Abstract
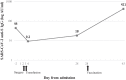
Objective: Vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 has been shown to be effective in preventing infection and severe disease. Massive bleeding and transfusion after vaccination can lead to a decrease in the antibody level. The effect of an additional dose of vaccine after blood transfusion has not been described previously. In this case report, we report the SARS-CoV-2 anti-S IgG trajectory in a male patient who received a third dose of vaccine after a massive postoperative bleed and blood and plasma transfusion.
Case presentation: A 57-year-old male physician had a SARS-CoV-2 anti-S IgG level of 44 AU/mL, measured using the Lumipulse Presto chemiluminescence assay 3 months after receiving 2 doses of the BNT162b2 vaccine. The patient underwent a hemicolectomy for colon cancer, experienced massive postoperative bleeding, and required a transfusion. The patient's SARS-CoV-2 anti-S IgG level dropped to 9.2 AU/mL. A third dose of BNT162b2 vaccination was administered to reduce the risk of breakthrough infection. Fifteen days after receiving the third vaccine dose, the patient's SARS-CoV-2 anti-S IgG level increased to 421 AU/mL, likely to reflect protection.
Conclusion: This report suggests that administering an extra dose of vaccine is useful for restoring protective antibody levels in vaccinated patients who experience massive postoperative bleeding.
Keywords: BNT162b2 vaccine; COVID-19; Massive bleeding; Plasma transfusion; SARS-CoV-2 anti-S IgG.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Healthcare Workers in South Korea Maintain a SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Response Six Months After Receiving a Second Dose of the BNT162b2 mRNA Vaccine.Front Immunol. 2022 Jan 31;13:827306. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.827306. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35173736 Free PMC article.
-
Immunogenicity of the BNT162b2 COVID-19 mRNA vaccine and early clinical outcomes in patients with haematological malignancies in Lithuania: a national prospective cohort study.Lancet Haematol. 2021 Aug;8(8):e583-e592. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3026(21)00169-1. Epub 2021 Jul 2. Lancet Haematol. 2021. PMID: 34224668 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in IgG Antibody Responses following BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines.Microbiol Spectr. 2021 Dec 22;9(3):e0116221. doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.01162-21. Epub 2021 Nov 10. Microbiol Spectr. 2021. PMID: 34756093 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in SARS-CoV-2-Specific Antibody Responses After the First, Second, and Third Doses of BNT162b2 in Naïve and Previously Infected Individuals: A 1-Year Observational Study in Healthcare Professionals.Front Immunol. 2022 May 27;13:876533. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.876533. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35711413 Free PMC article.
-
Pituitary apoplexy and COVID-19 vaccination: a case report and literature review.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Nov 17;13:1035482. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1035482. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36465651 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bergwerk M, Gonen T, Lustig Y, Amit S, Lipsitch M, Cohen C, Mandelboim M, Levin EG, Rubin C, Indenbaum V, Tal I, Zavitan M, Zuckerman N, Bar-Chaim A, Kreiss Y, Regev-Yochay G. Covid-19 breakthrough infections in vaccinated health care workers. N Engl J Med. 2021 Jul 28;385(16):1474–1484. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hibino M, Watanabe S, Kamada R, Tobe S, Maeda K, Horiuchi S, Kondo T. Antibody responses to the BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine in healthcare workers in a general hospital in Japan: A comparison of two assays for anti-spike protein immunoglobulin G. Intern Med. 2021 Dec 28 Online ahead of print. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

