The effects of Ginsenosides on PI3K/AKT signaling pathway
- PMID: 35220526
- PMCID: PMC9270311
- DOI: 10.1007/s11033-022-07270-y
The effects of Ginsenosides on PI3K/AKT signaling pathway
Abstract
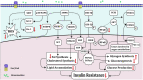
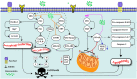
Ginsenosides belong to a group of steroid glycosides that are extracted from the plant genus Panax (ginseng). This plant has been used for a long time for the treatment of a variety of disorders in traditional medicine. Recent studies have assessed the biological impact of Ginsenosides in cell culture or animal models. Animal studies have shown their beneficial impacts in the remedy of pathological conditions in different tissues. The ameliorating effects of Ginsenosides in diverse pathogenic conditions can be attributed to their effects on the production of reactive oxygen species. These substances mainly affect the activity of AMPK/AKT and PI3K/AKT pathways. The beneficial effects of Ginsenosides have been appraised in diabetes-related complications, spinal cord injury, cerebral ischemia, myocardial ischemia, and other disorders which are associated with oxidative stress. Moreover, these substances have been shown to interfere with the pathologic conditions during carcinogenesis. In the current study, we explain these impacts in two distinct sections including non-neoplastic conditions and neoplastic conditions.
Keywords: Gene expression; Ginsenoside; Signaling pathway.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Attele AS, Wu JA, Yuan CS. Ginseng pharmacology: multiple constituents and multiple actions. Biochem Pharmacol. 1999;58(11):1685–1693. - PubMed
-
- Fuzzati N. Analysis methods of ginsenosides. J Chromatogr B. 2004;812:119–1331. - PubMed
-
- Nan F, Sun G, Xie W, Ye T, Sun X, Zhou P, et al. Ginsenoside Rb1 mitigates oxidative stress and apoptosis induced by methylglyoxal in SH-SY5Y cells via the PI3K/Akt pathway. Mol Cell Probes. 2019;48:101469. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

