A Retrospective Cohort Analysis of Treatment Patterns Over 1 Year in Patients with Psoriasis Treated with Ixekizumab or Guselkumab
- PMID: 35220545
- PMCID: PMC8941031
- DOI: 10.1007/s13555-022-00686-1
A Retrospective Cohort Analysis of Treatment Patterns Over 1 Year in Patients with Psoriasis Treated with Ixekizumab or Guselkumab
Abstract
Introduction: Persistence and adherence to psoriasis treatments reflect overall drug effectiveness, tolerability, and convenience. Limited data are available on the treatment patterns of ixekizumab, an interleukin (IL)-17A antagonist, vs. guselkumab, an IL-23 inhibitor. Our objective was to evaluate real-life psoriasis drug treatment patterns with ixekizumab vs. guselkumab.
Methods: This retrospective observational study used United States insurance claims data from IBM Watson MarketScan Databases to analyze treatment patterns (including adherence, persistence, time on monotherapy, switching, and use of concomitant medications) for patients with 1 year, ≥ 6 months, and up to 30 months of follow-up. Outcomes were compared between ixekizumab and guselkumab on the balanced sample after applying inverse probability of treatment weighting (IPTW).
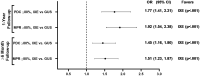
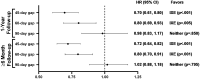
Results: Data for 1414 eligible patients (ixekizumab, N = 674 and guselkumab, N = 740) were assessed. Over the 1-year follow-up, adherence was greater for ixekizumab vs. guselkumab when evaluated by proportion of days covered ≥ 80% [odds ratio (OR) 1.77 (95% confidence interval, 1.41, 2.21), p < 0.001] and by medication possession ratio ≥ 80% [OR = 1.92 (1.54, 2.38), p < 0.001]. Persistence was longer for ixekizumab vs. guselkumab with a 60-day allowable gap [non-persistence hazard ratio (HR) (95% confidence interval): 0.80 (0.69, 0.93), p = 0.005], but there were no differences with a 90-day allowable gap [HR = 0.98 (0.83, 1.17), p = 0.850]. Results assessed in patients with ≥ 6 months follow-up confirmed these findings. This retrospective analysis of a United States claims database used prescription refill data to estimate persistence/adherence.
Conclusions: Based on real-world evidence using claims data, patients with psoriasis treated with ixekizumab had a greater adherence to and an equal or greater persistence with therapy vs. patients treated with guselkumab.
Keywords: Guselkumab; Ixekizumab; Psoriasis; Treatment adherence; Treatment discontinuation; Treatment persistence; Treatment switching.
Plain language summary
In real-world settings, how consistently patients take a drug (adherence) and how long they continue taking it (persistence) are thought to reflect patients’ satisfaction with the combination of efficacy and tolerability of the treatment. In this study of patients with psoriasis, we compared these measures—regularity of prescription refills and continued time on drug—between patients receiving ixekizumab or guselkumab for their psoriasis. This information was taken from a large insurance claims database, and so reflects results among commercially insured patients in the United States. We found that patients taking ixekizumab more consistently obtained prescription refills during the study period. Patients taking ixekizumab or guselkumab continued treatment for similar lengths of time when we allowed a longer gap of 90 days between prescription refills, but when a shorter gap of 60 days was allowed, those on ixekizumab spent a longer time on treatment. The findings were consistent regardless of prior treatment with other similar drugs (biologics). Overall, these findings indicate that for ixekizumab, which is dosed once every 4 weeks, and guselkumab, which is dosed once every 8 weeks, patients took ixekizumab more regularly and continued on the drug for about the same or a longer amount of time compared to patients taking guselkumab. These results may help dermatology practitioners in selecting biologic drugs for their patients with psoriasis.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparison of On-Label Treatment Persistence in Real-World Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis Receiving Guselkumab Versus Subcutaneous Interleukin-17A Inhibitors.Adv Ther. 2025 Feb;42(2):734-751. doi: 10.1007/s12325-024-03042-1. Epub 2024 Dec 2. Adv Ther. 2025. PMID: 39621228 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of real-world treatment patterns among patients with psoriasis prescribed ixekizumab or secukinumab.J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 Apr;82(4):927-935. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2019.11.015. Epub 2019 Nov 8. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020. PMID: 31712178
-
Comparison of Real-World Treatment Patterns Among Biologic-Experienced Patients with Psoriasis Treated with Ixekizumab or Secukinumab Over 18 Months.Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2021 Dec;11(6):2133-2145. doi: 10.1007/s13555-021-00627-4. Epub 2021 Oct 15. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2021. PMID: 34652590 Free PMC article.
-
Real-world evidence for ixekizumab in the treatment of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: literature review 2016-2021.J Dermatolog Treat. 2023 Dec;34(1):2160196. doi: 10.1080/09546634.2022.2160196. J Dermatolog Treat. 2023. PMID: 36629859 Review.
-
The Efficacy of Biologic Therapy for the Management of Palmoplantar Psoriasis and Palmoplantar Pustulosis: A Systematic Review.Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2017 Dec;7(4):425-446. doi: 10.1007/s13555-017-0207-0. Epub 2017 Nov 15. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2017. PMID: 29143230 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Guselkumab, Risankizumab, and Tildrakizumab in the Management of Hidradenitis Suppurativa: A Review of Existing Trials and Real-Life Data.Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2023 Sep 18;16:2525-2536. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S418748. eCollection 2023. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2023. PMID: 37745273 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long-Term Psoriasis Control with Guselkumab, Adalimumab, Secukinumab, or Ixekizumab in the USA.Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2023 Apr;13(4):1053-1068. doi: 10.1007/s13555-023-00910-6. Epub 2023 Mar 16. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2023. PMID: 36929120 Free PMC article.
-
Letter to the Editor: Response to Fitzgerald T et al. Long-Term Psoriasis Control with Guselkumab, Adalimumab, Secukinumab, or Ixekizumab in the USA.Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2023 Nov;13(11):2911-2916. doi: 10.1007/s13555-023-01015-w. Epub 2023 Sep 26. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2023. PMID: 37752409 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Matching-Adjusted Indirect Comparison of Risankizumab Versus Deucravacitinib in Patients with Moderate-to-Severe Plaque Psoriasis.Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2024 Nov;14(11):3071-3081. doi: 10.1007/s13555-024-01293-y. Epub 2024 Oct 25. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2024. PMID: 39453596 Free PMC article.
-
Long-Term Efficacy and Safety of Guselkumab for Moderate to Severe Psoriasis: A 3-Year Real-Life Retrospective Study.Psoriasis (Auckl). 2022 Jul 14;12:205-212. doi: 10.2147/PTT.S372262. eCollection 2022. Psoriasis (Auckl). 2022. PMID: 35859710 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Griffiths CE, Vender R, Sofen H, Kircik L, Tan H, Rottinghaus ST, et al. Effect of tofacitinib withdrawal and re-treatment on patient-reported outcomes: results from a Phase 3 study in patients with moderate to severe chronic plaque psoriasis. J Euro Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2017;31(2):323–332. doi: 10.1111/jdv.13808. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Reich K, Armstrong AW, Foley P, Song M, Wasfi Y, Randazzo B, et al. Efficacy and safety of guselkumab, an anti-interleukin-23 monoclonal antibody, compared with adalimumab for the treatment of patients with moderate to severe psoriasis with randomized withdrawal and retreatment: results from the phase III, double-blind, placebo- and active comparator-controlled VOYAGE 2 trial. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76(3):418–431. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2016.11.042. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

