Recovery of olfactory and gustatory dysfunctions in coronavirus disease 2019 patients: a prospective cohort study
- PMID: 35220983
- PMCID: PMC8886089
- DOI: 10.1017/S0022215121003935
Recovery of olfactory and gustatory dysfunctions in coronavirus disease 2019 patients: a prospective cohort study
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to determine the association of some demographic and clinical factors with recovery from olfactory and gustatory dysfunction in coronavirus disease 2019 patients in Iran.
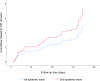
Methods: This prospective cohort study was performed on 242 coronavirus disease 2019 patients with olfactory and gustatory dysfunction. The time from onset to recovery for olfactory and gustatory dysfunction was estimated by the Kaplan-Meier estimator.
Results: After six months, 239 patients (98.8 per cent) had completely recovered from olfactory dysfunction. Olfactory and gustatory dysfunction symptoms resolved in 80.99 per cent and 83.56 per cent of the patients, respectively, within the first 30 days of symptom onset. Mean recovery time for olfactory dysfunction (35.07 ± 4.25 days) was significantly longer in those infected during the first epidemic wave compared with those infected during the second wave (21.65 ± 2.05 days) (p = 0.004). A similar pattern in recovery time was observed for cases of gustatory dysfunction (p = 0.005).
Conclusion: The recovery rate for coronavirus disease 2019 related olfactory and gustatory dysfunction is high within the first month of symptom onset.
Keywords: COVID-19; Cohort Studies; Recovery of Function; Smell; Taste Disorders.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Olfactory and Gustatory Dysfunctions as a Clinical Manifestation of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in a Malaysian Tertiary Center.Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2021 May;130(5):513-519. doi: 10.1177/0003489420963165. Epub 2020 Oct 7. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2021. PMID: 33025798
-
Long-standing gustatory and olfactory dysfunction in COVID-19 patients: a prospective study.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2022 Sep;279(9):4633-4640. doi: 10.1007/s00405-022-07428-1. Epub 2022 Jun 29. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2022. PMID: 35767055 Free PMC article.
-
Olfactory and gustatory dysfunctions as a clinical presentation of mild-to-moderate forms of the coronavirus disease (COVID-19): a multicenter European study.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2020 Aug;277(8):2251-2261. doi: 10.1007/s00405-020-05965-1. Epub 2020 Apr 6. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2020. PMID: 32253535 Free PMC article.
-
Sudden onset of olfactory and gustatory dysfunctions in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is momentous marker.Tzu Chi Med J. 2021 Jan 21;33(3):233-237. doi: 10.4103/tcmj.tcmj_238_20. eCollection 2021 Jul-Sep. Tzu Chi Med J. 2021. PMID: 34386359 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Olfactory and gustatory dysfunctions in COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2020 Sep;38(3):162-169. doi: 10.12932/AP-210520-0853. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32563232
Cited by
-
Virus load and incidence of olfactory, gustatory, respiratory, gastrointestinal disorders in COVID-19 patients: A retrospective cohort study.Clin Otolaryngol. 2021 Nov;46(6):1331-1338. doi: 10.1111/coa.13844. Epub 2021 Aug 16. Clin Otolaryngol. 2021. PMID: 34358409 Free PMC article.
-
Subjective and psychophysical olfactory and gustatory dysfunction among COVID-19 outpatients; short- and long-term results.PLoS One. 2022 Oct 3;17(10):e0275518. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0275518. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36191024 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Feng K, Yun Y, Wang X, Yang G, Zheng Y, Lin C et al. Analysis of CT features of 15 children with 2019 novel coronavirus infection [in Chinese]. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi 2020;58:275–8 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

