Evaluation of Caspase-3 and Ki-67 expression in squamous cell hyperplasia of the stomach induced by Platycodi radix water extract in Sprague-Dawley rats
- PMID: 35221495
- PMCID: PMC8828602
- DOI: 10.1293/tox.2021-0003
Evaluation of Caspase-3 and Ki-67 expression in squamous cell hyperplasia of the stomach induced by Platycodi radix water extract in Sprague-Dawley rats
Abstract
Platycodi radix is widely used in traditional herbal medicine for the treatment of bronchitis, asthma, pulmonary tuberculosis, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and diabetes. This study aimed to investigate cell proliferation (Ki-67) and apoptosis (Caspase-3) potential in squamous cell hyperplasia of the stomach induced by a Platycodi radix water extract in a subchronic toxicity study. One hundred formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded stomach tissues of rats treated with Platycodi radix at doses of 0, 500, 1,000, and 3,000 mg/kg body weight/day were used for the analysis. They were conventionally stained using hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and immunohistochemically (IHC) stained using caspase-3 and Ki-67 antibodies. The incidence of squamous cell hyperplasia was significantly increased in the 3,000 mg/kg b.w./day treatment group in both sexes (p<0.01). However, the hyperplastic change was completely repaired after 4 weeks of recovery period. Ki-67 expression was similar in all groups, with no statistically significant differences among the groups. Caspase-3 expression was significantly increased in both sexes in the 3,000 mg/kg b.w./day treatment group (p<0.01), compared with the vehicle control groups, and then reduced to normal levels in the recovery groups in both sexes. In conclusion, this study showed that squamous cell hyperplasia induced by the Platycodi radix water extract in the limiting ridge of the stomach is not considered to be abnormal proliferative change; as a result, squamous cell hyperplasia is considered to be a non-adverse effect when induced by the oral administration of the Platycodi radix water extract once daily for 13 weeks in rats.
Keywords: Caspase-3; Ki-67 antigen; Sprague–Dawley rats; local irritation; squamous cell hyperplasia.
©2022 The Japanese Society of Toxicologic Pathology.
Figures
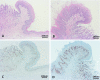
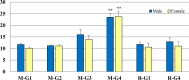
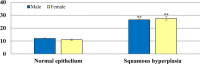
References
-
- Nolte T, Brander-Weber P, Dangler C, Deschl U, Elwell MR, Greaves P, Hailey R, Leach MW, Pandiri AR, Rogers A, Shackelford CC, Spencer A, Tanaka T, and Ward JM. Nonproliferative and proliferative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract, pancreas and salivary glands of the rat and mouse. J Toxicol Pathol. 29(Suppl): 1S–125S. 2016. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Urbańska N, Giebułtowicz J, Olszowska O, and Szypuła W. The growth and saponin production of Platycodon grandiflorum (Jacq.) A. DC. (Chinese bellflower) hairy roots cultures maintained in shake flasks and mist bioreactor. Acta Soc Bot Pol. 83. 2014.
-
- Cha S-B, Li Y, Bae J-S, Song S-W, Lee I-C, and Kim J-C. Evaluation of 13-week subchronic toxicity of Platycodon grandiflorus (Jacq.) A.DC. root extract in rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 267: 113621. 2021. - PubMed
-
- Jeong C-H, Choi GN, Kim JH, Kwak JH, Kim DO, Kim YJ, and Heo HJ. Antioxidant activities from the aerial parts of Platycodon grandiflorum. Food Chem. 118: 278–282. 2010.

