Receptor Interaction Profiles of 4-Alkoxy-3,5-Dimethoxy-Phenethylamines (Mescaline Derivatives) and Related Amphetamines
- PMID: 35222010
- PMCID: PMC8865417
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.794254
Receptor Interaction Profiles of 4-Alkoxy-3,5-Dimethoxy-Phenethylamines (Mescaline Derivatives) and Related Amphetamines
Abstract
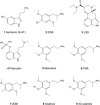
3,4,5-Trimethoxyphenethylamine (mescaline) is a psychedelic alkaloid found in peyote cactus. Related 4-alkoxy-3,5-dimethoxy-substituted phenethylamines (scalines) and amphetamines (3C-scalines) are reported to induce similarly potent psychedelic effects and are therefore potential novel therapeutics for psychedelic-assisted therapy. Herein, several pharmacologically uninvestigated scalines and 3C-scalines were examined at key monoamine targets in vitro. Binding affinity at human serotonergic 5-HT1A, 5-HT2A, and 5-HT2C, adrenergic α1A and α2A, and dopaminergic D2 receptors, rat and mouse trace amine-associated receptor 1 (TAAR1), and human monoamine transporters were assessed using target specific transfected cells. Furthermore, activation of human 5-HT2A and 5-HT2B receptors, and TAAR1 was examined. Generally, scalines and 3C-scalines bound with weak to moderately high affinity to the 5-HT2A receptor (K i = 150-12,000 nM). 3C-scalines showed a marginal preference for the 5-HT2A vs the 5-HT2C and 5-HT1A receptors whereas no preference was observed for the scalines. Extending the 4-alkoxy substituent increased 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors binding affinities, and enhanced activation potency and efficacy at the 5-HT2A but not at the 5-HT2B receptor. Introduction of fluorinated 4-alkoxy substituents generally increased 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors binding affinities and increased the activation potency and efficacy at the 5-HT2A and 5-HT2B receptors. Overall, no potent affinity was observed at non-serotonergic targets. As observed for other psychedelics, scalines and 3C-scalines interacted with the 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors and bound with higher affinities (up to 63-fold and 34-fold increase, respectively) when compared to mescaline.
Keywords: 3C-scalines; fluorination; mescaline; phenethylamine; psychedelic; scalines.
Copyright © 2022 Kolaczynska, Luethi, Trachsel, Hoener and Liechti.
Conflict of interest statement
DT is an employee of ReseaChem GmbH and MH is an employee of F. Hoffmann-La Roche. ML is a consultant for Mind Medicine, Inc. Knowhow associated with these substances investigated in this work is owned by Mind Medicine, Inc. Mind Medicine, Inc. had no role in financing, planning, or conducting the present research or the present publication. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Receptor Interaction Profiles of 4-Alkoxy-Substituted 2,5-Dimethoxyphenethylamines and Related Amphetamines.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Nov 28;10:1423. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01423. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31849671 Free PMC article.
-
Receptor interaction profiles of novel N-2-methoxybenzyl (NBOMe) derivatives of 2,5-dimethoxy-substituted phenethylamines (2C drugs).Neuropharmacology. 2015 Dec;99:546-53. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.08.034. Epub 2015 Aug 25. Neuropharmacology. 2015. PMID: 26318099
-
Monoamine receptor interaction profiles of 4-thio-substituted phenethylamines (2C-T drugs).Neuropharmacology. 2018 May 15;134(Pt A):141-148. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.07.012. Epub 2017 Jul 15. Neuropharmacology. 2018. PMID: 28720478
-
Dark Classics in Chemical Neuroscience: Mescaline.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2018 Oct 17;9(10):2448-2458. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.8b00215. Epub 2018 Jun 8. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29847089 Review.
-
An Overview on the Hallucinogenic Peyote and Its Alkaloid Mescaline: The Importance of Context, Ceremony and Culture.Molecules. 2023 Dec 5;28(24):7942. doi: 10.3390/molecules28247942. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 38138432 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Examining associations between MDMA/ecstasy and classic psychedelic use and impairments in social functioning in a U.S. adult sample.Sci Rep. 2023 Feb 11;13(1):2466. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-29763-x. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36774449 Free PMC article.
-
Binding and functional structure-activity similarities of 4-substituted 2,5-dimethoxyphenyl isopropylamine analogues at 5-HT2A and 5-HT2B serotonin receptors.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jan 24;14:1101290. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1101290. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36762110 Free PMC article.
-
Ligand-Free Signaling of G-Protein-Coupled Receptors: Physiology, Pharmacology, and Genetics.Molecules. 2023 Aug 31;28(17):6375. doi: 10.3390/molecules28176375. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37687205 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Predicting the Hallucinogenic Potential of Molecules Using Artificial Intelligence.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2024 Aug 21;15(16):3078-3089. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.4c00405. Epub 2024 Aug 2. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39092989 Free PMC article.
-
The Bright Side of Psychedelics: Latest Advances and Challenges in Neuropharmacology.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 10;24(2):1329. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021329. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36674849 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

