Apoptosis Triggering, an Important Way for Natural Products From Herbal Medicines to Treat Pancreatic Cancers
- PMID: 35222011
- PMCID: PMC8863938
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.796300
Apoptosis Triggering, an Important Way for Natural Products From Herbal Medicines to Treat Pancreatic Cancers
Abstract
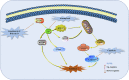
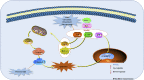
Pancreatic cancer, a poor prognosis and high morbidity and mortality cancer, is a malignant tumor occurring in pancreatic exocrine glands. Currently, surgery and gemcitabine (Gem) are commonly used to treat pancreatic cancers. However, the high recurrence rate and resistance makes the therapeutic effects still unsatisfied. Apoptosis is comprehensively recognized as one of the major ways of the programmed cell death, refers to the autonomous and orderly death process of cells in order to maintain the stability of the body's environment after receiving a certain signal or stimulation. Currently, it has also been proven to be a promising way for the treatment of pancreatic cancer. Nowadays, some active ingredients from herbal medicine have been reported to be effective for the treatment of pancreatic cancer via inducing cells apoptosis. Therefore, this article reviews the current references regarding anti pancreatic cancer effects of natural products derived from herbal medicines via triggering apoptosis, and summarizes the related potential signal pathways, including death receptors mediated apoptotic pathway, mitochondrial dependent apoptotic pathway, NF-κB mediated apoptotic pathways, MAPK mediated apoptotic pathway, ERS mediated apoptotic pathway, PI3K-Akt mediated apoptotic pathway, and other pathways such as JAK-STAT signal pathway, which can lay a certain foundation for the research and development of new natural products against pancreatic cancer.
Keywords: apoptosis; herbal medicine; natural products; pancreatic cancer; signal pathways.
Copyright © 2022 Li, Tang, Yang, Qian and Xu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Bondar V. M., Sweeney-Gotsch B., Andreeff M., Mills G. B., McConkey D. J. (2002). Inhibition of the Phosphatidylinositol 3'-Kinase-AKT Pathway Induces Apoptosis in Pancreatic Carcinoma Cells In Vitro and In Vivo . Mol. Cancer Ther. 1, 989–997. - PubMed
-
- Chen W. Y., Qin C. H., Tang F., Chen Y. (2020). Sinomenine Inhibits Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis of Pancreatic Cancer Capan-1 Cells by Regulating NF-Κb Signaling Pathway. Chin. J. Mod. Appl. Pharm. 37, 2190–2195. 10.13748/j.cnki.issn1007-7693.2020.18.003 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

