The Relationship Between Alexithymia and Mobile Phone Addiction Among Mainland Chinese Students: A Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 35222110
- PMCID: PMC8866180
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.754542
The Relationship Between Alexithymia and Mobile Phone Addiction Among Mainland Chinese Students: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
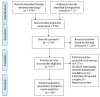
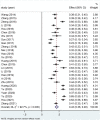
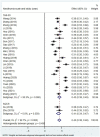
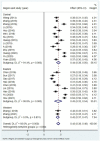
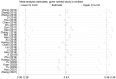
Alexithymia and mobile phone addiction are common phenomena in daily life. Many studies have explored the internal relationship between them based on different theoretical perspectives, but the extent of the exact correlation is still controversial. To address this controversy and clarify the reasons for the divergence, a meta-analysis of 26 articles comprising 23,387 Chinese students was conducted. The results show that alexithymia was highly positively correlated with mobile phone addiction (r = 0.41, 95% CI = [0.37, 0.45]). Furthermore, the relationship was moderated by mobile phone addiction measurement tool and year of publication, with studies using the Mobile Phone Addiction Tendency Scale (MPATS) having higher correlation coefficients than those using the Mobile Phone Addiction Index (MPAI) or other measurement tools. Studies published in 2020-2021 yielded higher correlations than those published in 2014-2016 and 2017-2019. However, the relationship was not moderated by gender, region, or measures of alexithymia. Therefore, our meta-analysis of available published data indicated that alexithymia and mobile phone addiction in Chinese students are not only highly positively correlated but also affected by mobile phone addiction measurement tools and publication year. Longitudinal studies or experimental studies should be strengthened in the future to further establish the direction(s) of causality for the relation between alexithymia and mobile phone addiction.
Keywords: alexithymia; mainland Chinese students; meta- analysis; mobile phone addiction; review.
Copyright © 2022 Huang, Wan, Lu, Ding and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Mobile Phone Addiction Mediates the Relationship Between Alexithymia and Learning Burnout in Chinese Medical Students: A Structural Equation Model Analysis.Psychol Res Behav Manag. 2021 Apr 12;14:455-465. doi: 10.2147/PRBM.S304635. eCollection 2021. Psychol Res Behav Manag. 2021. PMID: 33883952 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship Between Childhood Physical Abuse, Neglect and Alexithymia and Mobile Phone Addiction in Adolescents.Psychiatr Danub. 2022 Winter;34(4):653-659. doi: 10.24869/psyd.2022.653. Psychiatr Danub. 2022. PMID: 36548877
-
The relationship between college students' alexithymia and mobile phone addiction: Testing mediation and moderation effects.BMC Psychiatry. 2018 Oct 11;18(1):329. doi: 10.1186/s12888-018-1891-8. BMC Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 30309326 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between insecure attachment and mobile phone addiction: A meta-analysis.Addict Behav. 2022 Aug;131:107317. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2022.107317. Epub 2022 Mar 28. Addict Behav. 2022. PMID: 35413487 Review.
-
The correlation between mobile phone addiction and coping style among Chinese adolescents: a meta-analysis.Child Adolesc Psychiatry Ment Health. 2021 Oct 15;15(1):60. doi: 10.1186/s13034-021-00413-2. Child Adolesc Psychiatry Ment Health. 2021. PMID: 34654451 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The associations between smartphone addiction and self-esteem, self-control, and social support among Chinese adolescents: A meta-analysis.Front Psychol. 2022 Nov 7;13:1029323. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.1029323. eCollection 2022. Front Psychol. 2022. PMID: 36420390 Free PMC article.
-
The Association between Alexithymia and Social Media Addiction: Exploring the Role of Dysmorphic Symptoms, Symptoms Interference, and Self-Esteem, Controlling for Age and Gender.J Pers Med. 2023 Jan 12;13(1):152. doi: 10.3390/jpm13010152. J Pers Med. 2023. PMID: 36675813 Free PMC article.
-
Mobile phone addiction and mental health: the roles of sleep quality and perceived social support.Front Psychol. 2023 Sep 22;14:1265400. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1265400. eCollection 2023. Front Psychol. 2023. PMID: 37809316 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of physical exercise on mobile phone addiction among college students: a study based on Chinese universities.Front Psychol. 2025 Apr 14;16:1524520. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1524520. eCollection 2025. Front Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40297598 Free PMC article.
-
Network analysis of depression and anxiety symptoms and their associations with mobile phone addiction among Chinese medical students during the late stage of the COVID-19 pandemic.SSM Popul Health. 2023 Nov 23;25:101567. doi: 10.1016/j.ssmph.2023.101567. eCollection 2024 Mar. SSM Popul Health. 2023. PMID: 38524176 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Billieux J. Problematic use of the mobile phone: a literature review and a pathways model. Curr Psychiatry Rev. (2012) 8:299–307. 10.2174/157340012803520522 - DOI
-
- China Internet Network Information Centre (CINIC) . The 47th China Statistical Report on InternetDevelopment. (2015). Available online at: http://www.cnnic.cn/hlwfzyj/hlwxzbg/hlwtjbg/202102/P02021020333463348010...
-
- Shen X, Wang J-L. Loneliness and excessive smartphone use among Chinese college students: moderated mediation effect of perceived stressed and motivation. Comput Human Behav. (2019) 95:31–6. 10.1016/j.chb.2019.01.012 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

