Anti-Mouse CD83 Monoclonal Antibody Targeting Mature Dendritic Cells Provides Protection Against Collagen Induced Arthritis
- PMID: 35222372
- PMCID: PMC8866188
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.784528
Anti-Mouse CD83 Monoclonal Antibody Targeting Mature Dendritic Cells Provides Protection Against Collagen Induced Arthritis
Abstract
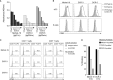
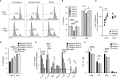
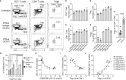
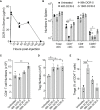
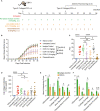
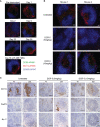
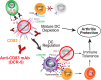
Antibodies targeting the activation marker CD83 can achieve immune suppression by targeting antigen-presenting mature dendritic cells (DC). This study investigated the immunosuppressive mechanisms of anti-CD83 antibody treatment in mice and tested its efficacy in a model of autoimmune rheumatoid arthritis. A rat anti-mouse CD83 IgG2a monoclonal antibody, DCR-5, was developed and functionally tested in mixed leukocyte reactions, demonstrating depletion of CD83+ conventional (c)DC, induction of regulatory DC (DCreg), and suppression of allogeneic T cell proliferation. DCR-5 injection into mice caused partial splenic cDC depletion for 2-4 days (mostly CD8+ and CD83+ cDC affected) with a concomitant increase in DCreg and regulatory T cells (Treg). Mice with collagen induced arthritis (CIA) treated with 2 or 6 mg/kg DCR-5 at baseline and every three days thereafter until euthanasia at day 36 exhibited significantly reduced arthritic paw scores and joint pathology compared to isotype control or untreated mice. While both doses reduced anti-collagen antibodies, only 6 mg/kg achieved significance. Treatment with 10 mg/kg DCR-5 was ineffective. Immunohistological staining of spleens at the end of CIA model with CD11c, CD83, and FoxP3 showed greater DC depletion and Treg induction in 6 mg/kg compared to 10 mg/kg DCR-5 treated mice. In conclusion, DCR-5 conferred protection from arthritis by targeting CD83, resulting in selective depletion of mature cDC and subsequent increases in DCreg and Treg. This highlights the potential for anti-CD83 antibodies as a targeted therapy for autoimmune diseases.
Keywords: CD83; antigen presentation; collagen induced arthritis (CIA); dendritic cells; monoclonal antibody; mouse; regulatory T cells.
Copyright © 2022 Silveira, Kupresanin, Romano, Hsu, Lo, Ju, Chen, Roberts, Baker and Clark.
Conflict of interest statement
PS, XJ, T-HL, AR and FK work for the Dendritic Cell Research laboratory which received sponsored research funding from Kira Biotech to undertake work quoted in this paper. HR derived a salary from Kira Biotech and has equity in the company. DB is a Director of Kira Biotech Pty Ltd. and has equity in the company. GC is a Non-Executive Director of Kira Biotech Pty Ltd. and Dendrocyte Pty Ltd. which has equity in Kira Biotech Pty Ltd. GC is Group Leader of the Dendritic Cell Research laboratory which received sponsored research funding to undertake work quoted in this paper. W-HH and H-TC declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

