S-Nitrosation of Arabidopsis thaliana Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 1 Prevents Its Irreversible Oxidation by Hydrogen Peroxide
- PMID: 35222471
- PMCID: PMC8867174
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2022.807249
S-Nitrosation of Arabidopsis thaliana Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 1 Prevents Its Irreversible Oxidation by Hydrogen Peroxide
Abstract
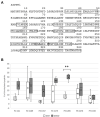
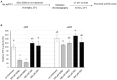
Tyrosine-specific protein tyrosine phosphatases (Tyr-specific PTPases) are key signaling enzymes catalyzing the removal of the phosphate group from phosphorylated tyrosine residues on target proteins. This post-translational modification notably allows the regulation of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascades during defense reactions. Arabidopsis thaliana protein tyrosine phosphatase 1 (AtPTP1), the only Tyr-specific PTPase present in this plant, acts as a repressor of H2O2 production and regulates the activity of MPK3/MPK6 MAPKs by direct dephosphorylation. Here, we report that recombinant histidine (His)-AtPTP1 protein activity is directly inhibited by H2O2 and nitric oxide (NO) exogenous treatments. The effects of NO are exerted by S-nitrosation, i.e., the formation of a covalent bond between NO and a reduced cysteine residue. This post-translational modification targets the catalytic cysteine C265 and could protect the AtPTP1 protein from its irreversible oxidation by H2O2. This mechanism of protection could be a conserved mechanism in plant PTPases.
Keywords: Arabidopsis thaliana; H2O2; S-nitrosation; mitogen-activated protein kinases; nitric oxide; oxidation; post-translational modifications; protein tyrosine phosphatase 1.
Copyright © 2022 Nicolas-Francès, Rossi, Rosnoblet, Pichereaux, Hichami, Astier, Klinguer, Wendehenne and Besson-Bard.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Astier J., Besson-Bard A., Lamotte O., Bertoldo J., Bourque S., Terenzi H., et al. (2012). Nitric oxide inhibits the ATPase activity of the chaperone-like AAA+ ATPase CDC48, a target for S-nitrosylation in cryptogein signalling in tobacco cells. Biochem. J. 447, 249–260. doi: 10.1042/BJ20120257, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bartels S., Anderson J. C., González Besteiro M. A., Carreri A., Hirt H., Buchala A., et al. (2009). MAP KINASE PHOSPHATASE1 and PROTEIN TYROSINE PHOSPHATASE1 are repressors of salicylic acid synthesis and snc1-mediated responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 21, 2884–2897. doi: 10.1105/tpc.109.067678, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Charbonneau H., Tonks N. K., Kumar S., Diltz C. D., Harrylock M., Cool D. E., et al. (1989). Human placenta protein-tyrosine-phosphatase: amino acid sequence and relationship to a family of receptor-like proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 86, 5252–5256. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5252, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

