LACTB suppresses carcinogenesis in lung cancer and regulates the EMT pathway
- PMID: 35222724
- PMCID: PMC8815028
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2022.11172
LACTB suppresses carcinogenesis in lung cancer and regulates the EMT pathway
Abstract
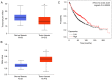
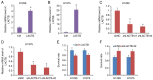
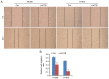
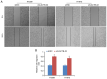
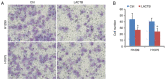
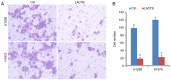
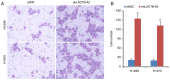
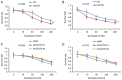
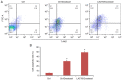
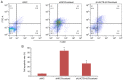
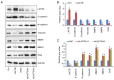
Lung cancer causes thousands of deaths worldwide every year, and present therapeutics show little benefit for advanced-stage patients. Researchers do not know why and how lung cancer begins. Lactamase β (LACTB) is a tumor-suppressor in some cancers. However, its role in lung cancer is unknown. By analyzing the TCGA database and Kaplan-Meier Plotter database, LACTB was found to be downregulated in lung cancer tissues but the methylation level was increased. Patients with high LACTB expression exhibited improved survival. Then, in vitro assays demonstrated that LACTB overexpression inhibited cell migration and invasion, and induced apoptosis in H1299 and H1975 cells. Knockdown of LACTB caused the reverse effects. Moreover, a much higher apoptotic rate and more potent inhibitory effects on H1299 and H1975 cells were obtained when LACTB was combined with docetaxel. In addition, members of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) signaling pathway were assessed using western blot analysis. The expression of E-cadherin was decreased while levels of N-cadherin and vimentin were increased after knockdown of LACTB in lung cancer cells. By contrast, overexpression of LACTB increased the level of E-cadherin but decreased N-cadherin and vimentin. Therefore, LACTB is a tumor suppressor in lung cancer that inhibits cell migration and invasion and induces cell apoptosis. Meanwhile, LACTB was found to strengthen the anticancer role of docetaxel and to suppress the EMT pathway in lung cancer.
Keywords: LACTB; docetaxel; epithelial-mesenchymal transition; lung cancer.
Copyright: © Xu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
