LINC00460 Stimulates the Proliferation of Vascular Endothelial Cells by Downregulating miRNA-24-3p
- PMID: 35222741
- PMCID: PMC8881155
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/2524156
LINC00460 Stimulates the Proliferation of Vascular Endothelial Cells by Downregulating miRNA-24-3p
Abstract
Objective: To clarify the effect of LINC00460 on mediating the proliferative ability of vascular endothelial cells (ECs) by targeting microRNA-24-3p (miRNA-24-3p), thus influencing the progression of atherosclerotic diseases.
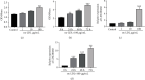
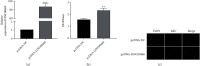
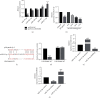
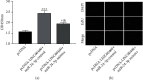
Methods: Relative levels of LINC00460 and miRNA-24-3p in ECs induced with different doses of ox-LDL (oxidized low density lipoprotein) for different time points were determined by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). Influences of LINC00460 and miRNA-24-3p on the viability of ECs were assessed by Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) and 5-ethynyl-2'-deoxyuridine (EdU) assay. Through dual-luciferase reporter gene assay, the binding between LINC00460 and miRNA-24-3p was evaluated. At last, rescue experiments were performed to identify the function of the LINC00460/miRNA-24-3p axis in regulating the proliferative ability of ECs.
Results: LINC00460 was upregulated after ox-LDL treatment in a dose- and time-dependent manner. Viability of ECs gradually increased with the prolongation of ox-LDL treatment and the treatment of increased dose. The overexpression of LINC00460 enhanced the viability and EdU-positive rate in ECs treated with ox-LDL. miRNA-24-3p was the direct target of LINC00460, which was negatively regulated by LINC00460. miRNA-24-3p was downregulated with the prolongation of ox-LDL treatment. The overexpression of miRNA-24-3p could reverse the effect of LINC00460 on regulating the proliferative ability of ECs.
Conclusions: LINC00460 regulates the proliferative ability of ECs and thus the occurrence and development of coronary atherosclerotic diseases by targeting miRNA-24-3p.
Copyright © 2022 Ruofei Jia et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Leong D. P., Joseph P. G., McKee M., et al. Reducing the global burden of cardiovascular disease, part 2: prevention and treatment of cardiovascular disease. Circulation Research . 2017;121(6):695–710. - PubMed
-
- Jokinen E. Obesity and cardiovascular disease. Minerva Pediatrica . 2015;67(1):25–32. - PubMed
-
- Aggarwal M., Aggarwal B., Rao J. Integrative medicine for cardiovascular disease and prevention. The Medical Clinics of North America . 2017;101(5):895–923. - PubMed
-
- Berinstein E., Levy A. Recent developments and future directions for the use of pharmacogenomics in cardiovascular disease treatments. Expert Opinion on Drug Metabolism & Toxicology . 2017;13(9):973–983. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

