The Effectiveness of Traditional Chinese Medicine Combined With Surgery to Treat Granulomatous Mastitis: A Propensity-Matched Analysis
- PMID: 35223513
- PMCID: PMC8866696
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.833742
The Effectiveness of Traditional Chinese Medicine Combined With Surgery to Treat Granulomatous Mastitis: A Propensity-Matched Analysis
Abstract
Purpose: The etiology and pathology of granulomatous mastitis (GLM) are still unknown. Expert consensus on the treatment of GLM has not been developed. The objective of this study is to study the effectiveness of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) combined with surgery in treating GLM.
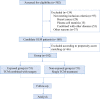
Materials and methods: A retrospective cohort study was implemented at Longhua Hospital of Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine in China between September 2019 and August 2021. Female patients were included according to the propensity-score matching (PSM) method and balanced according to age and BMI. Patients with GLM diagnosed by pathology and a course of disease ≥ 6 months were included in this trial. Patients were divided into the TCM alone group or TCM + surgery group.
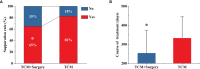
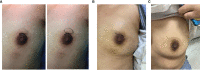
Results: In total, 168 female patients were assessed and 102 patients were included in the study after PSM (51 in the TCM group and 51 in the TCM + surgery group). The average age of the patients was 32 years (21-47 years). There was no significant baseline characteristics difference between two groups after PSM. The suppuration rate in the TCM + surgery group was less than that in the TCM group (64.7% vs. 83.35%, P < 0.05), and the TCM + surgery group had a higher 9-month cure rate than the TCM group (86.3% vs. 52.9%, P < 0.05). The full course of disease in the TCM + surgery group was shorter than that in the TCM group (253.9 ± 117.3 days vs. 332.5 ± 111.6 days, P < 0.05).
Conclusions: TCM combined with surgery can improve the cure rate and shorten the full course of GLM treatment, indicating surgery should be integrated in the clinical management of GLM.
Keywords: clinical outcome; granulomatous mastitis; integrated Chinese and Western surgery; surgery; traditional Chinese medicine.
Copyright © 2022 Sawuer, Wu, Sun and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous