Methodology Establishment and Application of VITEK Mass Spectrometry to Detect Carbapenemase-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae
- PMID: 35223536
- PMCID: PMC8873529
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.761328
Methodology Establishment and Application of VITEK Mass Spectrometry to Detect Carbapenemase-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae
Abstract
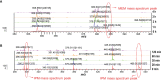
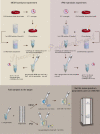
The ability of VITEK mass spectrometry (MS) in detection of bacterial resistance is currently under exploration and evaluation. In this study, we developed and validated a VITEK MS method to rapidly test carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae (CPKP). Solvents, antibiotic concentrations, crystal conditions and times, centrifugation speeds, and other factors were optimized to design a rapid sample pretreatment process for CPKP detection by VITEK MS. The related parameters of the mass spectrum were adjusted on the instrument to establish an CPKP detection mode. 133 clinically isolated strains of CPKP in the microbiology laboratory at the Shenzhen People's Hospital from 2004 to 2017 were selected for accuracy evaluation. The fresh suspected strains from the microbiology laboratory in 2020 were used to complete the clinical verification. Two antibiotics, meropenem (MEM) and imipenem (IPM), were used as substrates. These two substrates were incubated with suspected CPKP, and the results were obtained by VITEK MS detection. Using this method, different types of CPKP showed different detection results and all the CPKP strains producing KPC-2 and IMP-4 carbapenemase were detected by VITEK MS. Thus, VITEK MS can be used for rapid detection of CPKP, especially for some common types of CPKP. This method provides high accuracy and speed of detection. Combined with its cost advantages, it can be intensely valuable in clinical microbiology laboratories after the standard operating procedures are determined.
Keywords: IPM; MALDI-TOF MS; MEM; VITEK MS; carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae; hydrolysis experiment; imipenem; meropenem.
Copyright © 2022 Lin, Hu, Wu, Lu, Chen and Wu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Axelsson C., Rehnstam-Holm A. S., Nilson B. (2020). Rapid Detection of Antibiotic Resistance in Positive Blood Cultures by MALDI-TOF MS and an Automated and Optimized MBT-ASTRA Protocol for Escherichia Coli and Klebsiella Pneumoniae. Infect. Dis. (Auckl) 52, 45–53. doi: 10.1080/23744235.2019.1682658 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

