MiRNA-21 Regulates Bronchial Epithelial Cell Proliferation by Activating Tgfβ1/Smad Signaling Pathway and Its Correlation with Asthma Severity in Children
- PMID: 35223564
- PMCID: PMC8819233
- DOI: 10.18502/ijph.v50i10.7497
MiRNA-21 Regulates Bronchial Epithelial Cell Proliferation by Activating Tgfβ1/Smad Signaling Pathway and Its Correlation with Asthma Severity in Children
Abstract
Background: This research was designed to probe into the role of miRNA-21 in the pathogenesis of childhood asthma and its correlation with the severity.
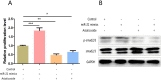
Methods: Fifty-four children with bronchial asthma admitted to the Third Affiliated Hospital of Qiqihar Medical University from Jun 2018 to Dec 2019 were included. Forty nine healthy children underwent physical examination at this time period were also enrolled. The miR-21 expression in peripheral blood serum was analyzed by qRT-PCR. The relationship between the expression and severity of asthma in children was explored by Spearman correlation analysis and ROC curve. Bronchial epithelial cell lines were cultured in vitro and divided into blank control group, negative control group and miR-21 inhibition and activation group. The changes of cell proliferation after treatment were detected by CCK-8 test in different groups. The expression of TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway protein in cells was assessed by Western blot (WB).
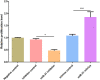
Results: Compared with that of healthy children, the miR-21 expression in peripheral blood serum of asthmatic children was higher (P<0.001). MiR-21 expression was positively correlated with the severity of illness (r=0.853, P<0.001). The results of cell experiments in vitro signified that miR-21 can promote the proliferation of bronchial epithelial cells, and may be involved in regulating the expression of TGF-β1/Smad3 signaling pathway, thus affecting cell proliferation.
Conclusion: miRNA-21 regulates the proliferation of bronchial epithelial cells by activating TGFβ1/Smad signaling pathway. And it is positively correlated with the severity of asthma in children.
Keywords: Childhood asthma; MicroRNA; Proliferation; Transforming growth factor β1.
Copyright © 2021 Kang et al. Published by Tehran University of Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Barnes PJ. (2018). Targeting cytokines to treat asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Nat Rev Immunol, 18(7): 454–466. - PubMed
-
- Tarlo SM, Malo JL. (2006). An ATS/ERS report: 100 key questions and needs in occupational asthma. Eur Respir J, 27(3): 607–614. - PubMed
-
- National Cooperative Group on Childhood Asthma; Institute of Environmental Health and Related Product Safety, Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention (2013). Third nationwide survey of childhood asthma in urban areas of China. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi, 51(10): 729–735. - PubMed
-
- GBD 2015 Chronic Respiratory Disease Collaborators (2017). Global, regional, and national deaths, prevalence, disability-adjusted life years, and years lived with disability for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma, 1990–2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet Respir Med, 5(9): 691–706. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tai A, Tran H, Roberts M, et al. (2014). Outcomes of childhood asthma to the age of 50 years. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 133(6): 1572–8.e3. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
