Intimate Partner Violence Victimization Influences Suicidal Ideation via Interpersonal Dependency and Anger
- PMID: 35223602
- PMCID: PMC8826317
- DOI: 10.18502/ijph.v50i11.7583
Intimate Partner Violence Victimization Influences Suicidal Ideation via Interpersonal Dependency and Anger
Abstract
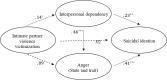
Background: Intimate partner violence is a serious global social problem. While intimate partner violence is highly prevalent, few studies have examined its negative outcomes among victims in South Korea. The aim was to clarify the mediating roles of interpersonal dependency and anger on the relationship between intimate partner violence victimization and suicidal ideation.
Methods: In this descriptive, cross-sectional study, 301 participants (203 women and 98 men) aged 18-65 yr completed an online questionnaire on a social networking site. Data were collected between Feb and Mar 2017 in South Korea. Structural equation modeling was used to test the fitness of the conceptual model of this study.
Results: We found significant correlations between intimate partner violence victimization, interpersonal dependency, state-trait anger, and suicidal ideation. Intimate partner violence victimization influenced anger and suicidal ideation only when the victims had high interpersonal dependency.
Conclusion: It is necessary to develop programs for reducing interpersonal dependency and improving anger management that are specifically targeted at intimate partner violence victims to prevent suicidal ideation.
Keywords: Interpersonal dependency; Mediating effect; State anger; Trait anger.
Copyright © 2021 Ha et al. Published by Tehran University of Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests.
Figures
References
-
- García-Moreno C, Pallitto C, Devries K, Stöckl H, Watts C, Abrahams N. (2013). Global and regional estimates of violence against women: prevalence and health effects of intimate partner violence and non-partner sexual violence: World Health Organization; 2013. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/85239
-
- Renner LM, Whitney SD. (2012). Risk factors for unidirectional and bidirectional intimate partner violence among young adults. Child Abuse Negl, 36(1):40–52. - PubMed
-
- Costa D, Soares J, Lindert J, et al. (2015). Intimate partner violence: a study in men and women from six European countries. Int J Public Health, 60(4):467–78. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources