Effects of Combing Group Executive Functioning and Online Parent Training on School-Aged Children With ADHD: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 35223713
- PMCID: PMC8874140
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2021.813305
Effects of Combing Group Executive Functioning and Online Parent Training on School-Aged Children With ADHD: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
Objective: The acceptance of drug treatment for younger children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in China remains low. Here, we explored the clinical benefits of a non-pharmaceutical intervention method combining a group and executive function training and an online parent training program, termed group executive functioning and online parent training (GEF-OPT), for school-aged students with ADHD through a randomized controlled trial.
Method: A total of 145 children (aged 6-8 years) were formally registered and randomized to the intervention group (n = 73) and waitlist group (n = 72). The enrolled children received eight sessions of GEF-OPT treatment, which consists of a hospital-based children executive function (EF) training program and an online parent training program. Treatment outcome was assessed by a parent/teacher report questionnaire and neurophysiological experiment.
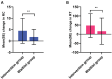
Results: After eight sessions of intervention, children in the intervention group showed a significant improvement in inattentive symptom compared to the waitlist group (14.70 ± 4.35 vs. 16.03 ± 2.93; p = 0.024), but an insignificant difference in hyperactive-impulsivity (9.85 ± 5.30 vs. 10.69 ± 5.10; p = 0.913). Comorbid oppositional defiant disorder was significantly reduced in the intervention group (7.03 ± 4.39 vs. 8.53 ± 4.41; p = 0.035). Children in the intervention group had greater reduction in the scores of behavioral regulation index (inhibition, emotional control) and metacognition index (working memory, planning/organization, monitoring) in executive function than those in the waitlist group (p < 0.05). Significant effects were also found in learning problem of Weiss Functional Impairment Scale-Parent form and parental distress between two groups at post-treatment (p < 0.05). In line with this, the result of go/no-go task showed significant improvements in accuracy change (4.45 ± 5.50% vs. 1.76 ± 3.35%; p = 0.001) and reaction time change (47.45 ± 62.25 s vs. 16.19 ± 72.22 s; p = 0.007) in the intervention group compared with the waitlist group.
Conclusion: We conclude that participants in the GEF-OPT program improved outcomes for inattentive symptom, executive function, learning problems, and parental distress. GEF-OPT is a promising non-pharmaceutical therapeutic option for younger children.
Trial registration: ChiCTR2100052803.
Keywords: ADHD; executive function; non-pharmacological treatment; online intervention; parent training.
Copyright © 2022 Chu, Zhu, Ma, Pan, Shen, Wu, Wang and Yu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The handling editor FL declared a shared parent affiliation with the authors at the time of the review.
Figures
References
-
- Catala-Lopez F, Hutton B, Nunez-Beltran A, Page MJ, Ridao M, Macias Saint-Gerons D, et al. . The pharmacological and non-pharmacological treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents: a systematic review with network meta-analyses of randomised trials. PLoS ONE. (2017) 12:e0180355. 10.1371/journal.pone.0180355 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

