Protein Posttranslational Signatures Identified in COVID-19 Patient Plasma
- PMID: 35223838
- PMCID: PMC8873527
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2022.807149
Protein Posttranslational Signatures Identified in COVID-19 Patient Plasma
Abstract
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) is a highly contagious virus of the coronavirus family that causes coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19) in humans and a number of animal species. COVID-19 has rapidly propagated in the world in the past 2 years, causing a global pandemic. Here, we performed proteomic analysis of plasma samples from COVID-19 patients compared to healthy control donors in an exploratory study to gain insights into protein-level changes in the patients caused by SARS-CoV-2 infection and to identify potential proteomic and posttranslational signatures of this disease. Our results suggest a global change in protein processing and regulation that occurs in response to SARS-CoV-2, and the existence of a posttranslational COVID-19 signature that includes an elevation in threonine phosphorylation, a change in glycosylation, and a decrease in arginylation, an emerging posttranslational modification not previously implicated in infectious disease. This study provides a resource for COVID-19 researchers and, longer term, and will inform our understanding of this disease and its treatment.
Keywords: COVID-19; arginylation; peptidomics; posttranslational modifications; proteomics.
Copyright © 2022 Vedula, Tang, Speicher and Kashina.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
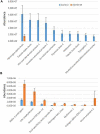
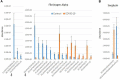
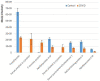

References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

