The Nrf2 Pathway in Liver Diseases
- PMID: 35223849
- PMCID: PMC8866876
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2022.826204
The Nrf2 Pathway in Liver Diseases
Abstract
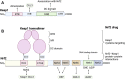
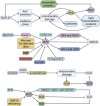
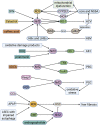
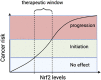
Oxidative stress is the leading cause of most liver diseases, such as drug-induced liver injury, viral hepatitis, and alcoholic hepatitis caused by drugs, viruses, and ethanol. The Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1-NFE2-related factor 2 (Keap1-Nrf2) system is a critical defense mechanism of cells and organisms in response to oxidative stress. Accelerating studies have clarified that the Keap1-Nrf2 axis are involved in the prevention and attenuation of liver injury. Nrf2 up-regulation could alleviate drug-induced liver injury in mice. Moreover, many natural Nrf2 activators can regulate lipid metabolism and oxidative stress of liver cells to alleviate fatty liver disease in mice. In virus hepatitis, the increased Nrf2 can inhibit hepatitis C viral replication by up-regulating hemeoxygenase-1. In autoimmune liver diseases, the increased Nrf2 is essential for mice to resist liver injury. In liver cirrhosis, the enhanced Nrf2 reduces the activation of hepatic stellate cells by reducing reactive oxygen species levels to prevent liver fibrosis. Nrf2 plays a dual function in liver cancer progression. At present, a Nrf2 agonist has received clinical approval. Therefore, activating the Nrf2 pathway to induce the expression of cytoprotective genes is a potential option for treating liver diseases. In this review, we comprehensively summarized the relationships between oxidative stress and liver injury, and the critical role of the Nrf2 pathway in multiple liver diseases.
Keywords: kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1; liver diseases; nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor 2; oxidative stress; reactive oxygen species.
Copyright © 2022 Zhou, Zheng and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Hepatocyte-specific NRF2 activation controls fibrogenesis and carcinogenesis in steatohepatitis.J Hepatol. 2021 Mar;74(3):638-648. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.09.037. Epub 2020 Oct 24. J Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 33342543
-
Role of Nrf2 in preventing ethanol-induced oxidative stress and lipid accumulation.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2012 Aug 1;262(3):321-9. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2012.05.010. Epub 2012 May 22. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22627062
-
Inhibition of autophagy reverses alcohol-induced hepatic stellate cells activation through activation of Nrf2-Keap1-ARE signaling pathway.Biochimie. 2018 Apr;147:55-62. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2017.12.013. Epub 2018 Jan 2. Biochimie. 2018. PMID: 29305174
-
Targeting the KEAP1-NRF2 System to Prevent Kidney Disease Progression.Am J Nephrol. 2017;45(6):473-483. doi: 10.1159/000475890. Epub 2017 May 13. Am J Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 28502971 Review.
-
The KEAP1-NRF2 System in Healthy Aging and Longevity.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Nov 30;10(12):1929. doi: 10.3390/antiox10121929. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34943032 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
C-phycocyanin alleviated cisplatin-induced oxidative stress and inflammation via gut microbiota-metabolites axis in mice.Front Nutr. 2022 Sep 20;9:996614. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.996614. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 36225866 Free PMC article.
-
New perspectives on the therapeutic potential of quercetin in non-communicable diseases: Targeting Nrf2 to counteract oxidative stress and inflammation.J Pharm Anal. 2024 Jun;14(6):100930. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2023.12.020. Epub 2024 Jan 3. J Pharm Anal. 2024. PMID: 39005843 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Selenium nanoparticles mitigate chlorpyrifos-induced nephrotoxicity by modulating oxidative stress, inflammation, and the SIRT1/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway.J Mol Histol. 2025 Jul 31;56(4):249. doi: 10.1007/s10735-025-10487-3. J Mol Histol. 2025. PMID: 40742471 No abstract available.
-
Novel insights into bexarotene's role in preventing cholestasis: mechanisms and implications.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Aug;398(8):10495-10508. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-03917-2. Epub 2025 Feb 26. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40009169
-
Proanthocyanidins-Based Synbiotics as a Novel Strategy for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Risk Reduction.Molecules. 2024 Feb 3;29(3):709. doi: 10.3390/molecules29030709. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38338453 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bailey S. M., Cunningham C. C. (2002). Contribution of Mitochondria to Oxidative Stress Associated with Alcoholic Liver Disease1 1This Article Is Part of a Series of Reviews on "Alcohol, Oxidative Stress and Cell Injury". The Full List of Papers May Be Found on the Homepage of the Journal. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 32 (1), 11–16. 10.1016/s0891-5849(01)00769-9 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

