Comparison of a New Optical Biometer That Combines Scheimpflug Imaging With Partial Coherence Interferometry With That of an Optical Biometer Based on Swept-Source Optical Coherence Tomography and Placido-Disk Topography
- PMID: 35223885
- PMCID: PMC8866319
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2021.814519
Comparison of a New Optical Biometer That Combines Scheimpflug Imaging With Partial Coherence Interferometry With That of an Optical Biometer Based on Swept-Source Optical Coherence Tomography and Placido-Disk Topography
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate measurement precision and to compare the Pentacam AXL (Oculus Optikgeräte, Wetzlar, German), a new optical biometer based on Scheimpflug imaging and partial coherence interferometry (PCI) with that of the OA-2000 biometer (Tomey, Nagoya, Japan), which combines swept-source optical coherence tomography (SS-OCT) and Placido-disk topography.
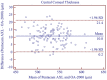
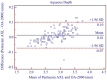
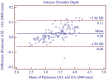
Methods: Axial length (AL), central corneal thickness (CCT), anterior chamber depth (ACD), aqueous depth (AQD), mean keratometry (Km), astigmatism vectors J0, J45, and corneal diameter (CD) were measured in triplicate by two technical operators. Within-subject standard deviation (Sw), repeatability and reproducibility (2.77 Sw), coefficient of variation (CoV), and intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) were used to assess the Pentacam AXL intra-observer repeatability and inter-observer reproducibility. Paired t-test and Bland-Altman plots were used to determine the agreement between the two biometers.
Results: The new optical biometer had high intra-observer repeatability [all parameters evaluated had low CoV (<0.71%) and high ICC (>0.88)]. Inter-observer reproducibility was also excellent, with high ICC (>0.95) and low CoV (<0.52%). The 95% LoA between the new biometer and OA-2000 were insignificant for most of the parameters evaluated, especially for AL. However, the measurement agreement was moderate for CCT.
Conclusions: Intra-observer repeatability and inter-observer reproducibility were excellent for all parameters evaluated using the new optical biometer based on Scheimpflug imaging and PCI. There was a high agreement between the two devices and hence could be clinically interchangeable for the measurement of most ocular parameters.
Keywords: Scheimpflug imaging; agreement; repeatability; reproducibility; swept source optical coherence tomography.
Copyright © 2022 Chen, Zhang, Savini, Zhang, Huang, Yu, Wang, Ning, Huang and Tu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

