Impact of Succinylcholine vs. Rocuronium on Apnea Duration for Rapid Sequence Induction: A Prospective Cohort Study
- PMID: 35223887
- PMCID: PMC8864070
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2022.717477
Impact of Succinylcholine vs. Rocuronium on Apnea Duration for Rapid Sequence Induction: A Prospective Cohort Study
Abstract
Objective: The present study aimed to evaluate the impact of 1.5 mg/kg succinylcholine or 1.2 mg/kg rocuronium, vs. 1.0 mg/kg succinylcholine on apnea duration in patients underwent rapid sequence induction (RSI).
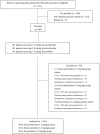
Methods: This prospective cohort study was conducted in the Department of Anesthesiology in Shanghai General Hospital from July 2020 to November 2020. Apnea duration was defined as the time from apnea prompted by the PETCO2 waveform to the time the point of oxygen saturation declined to 90% (T90) and 95% (T95) after succinylcholine or rocuronium administration. The primary outcome included T90 and T95 changes in 1.5 mg/kg vs. 1.0 mg/kg succinylcholine groups and 1.5 mg/kg succinylcholine vs. 1.2 mg/kg rocuronium groups.
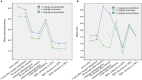
Results: A total of 265 participants were subjected for analysis. The succinylcholine (1.0 mg/kg) group had a significantly longer T90 (50.72, 95% confidence interval [CI, 7.60, 94.38], P = 0.015) and T95 (48.09, 95% CI [7.11, 89.07], P = 0.012) than the succinylcholine (1.5 mg/kg) group. In addition, significantly longer T90 (56.84, 95% CI [16.24, 97.44], P = 0.003) and T95 (50.57, 95% CI [12.58, 88.57], P = 0.003) were observed in the rocuronium (1.2 mg/kg) group than those in the succinylcholine (1.5 mg/kg) group. No severe side events were observed during the operation.
Conclusion: Rocuronium and the lower dose of succinylcholine may be recommended to patients underwent RSI.
Keywords: apnea duration; oxygen saturation; rapid sequence induction intubation; rocuronium; succinylcholine.
Copyright © 2022 Tang, Zhao, Li, Huang, Li, Chen and Huang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Desaturation following rapid sequence induction using succinylcholine vs. rocuronium in overweight patients.Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2011 Feb;55(2):203-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.2010.02365.x. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2011. PMID: 21226862 Clinical Trial.
-
Succinylcholine versus rocuronium for rapid sequence intubation in intensive care: a prospective, randomized controlled trial.Crit Care. 2011 Aug 16;15(4):R199. doi: 10.1186/cc10367. Crit Care. 2011. PMID: 21846380 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Post-intubation analgesia and sedation following succinylcholine vs. rocuronium in the emergency department.Am J Emerg Med. 2023 Sep;71:99-103. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2023.06.017. Epub 2023 Jun 16. Am J Emerg Med. 2023. PMID: 37356339
-
Pharmacotherapy optimization for rapid sequence intubation in the emergency department.Am J Emerg Med. 2023 Aug;70:19-29. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2023.05.004. Epub 2023 May 10. Am J Emerg Med. 2023. PMID: 37196592 Review.
-
Rocuronium vs. succinylcholine for rapid sequence intubation: a Cochrane systematic review.Anaesthesia. 2017 Jun;72(6):765-777. doi: 10.1111/anae.13903. Anaesthesia. 2017. PMID: 28654173
Cited by
-
Advancing anesthesiology trainee proficiency in airway management via simulation-based training: a non-hypoxic apnea duration approach.PeerJ. 2025 Jun 4;13:e19555. doi: 10.7717/peerj.19555. eCollection 2025. PeerJ. 2025. PMID: 40487061 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A Randomized Double-Blind Comparative Study of the Intubating Conditions and Hemodynamic Effects of Rocuronium and Succinylcholine in Pediatric Patients.Cureus. 2023 Sep 4;15(9):e44631. doi: 10.7759/cureus.44631. eCollection 2023 Sep. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37799234 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

