A Novel Three-Dimensional and Tissue Doppler Echocardiographic Index for Diagnosing and Prognosticating Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction
- PMID: 35224053
- PMCID: PMC8866454
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.822314
A Novel Three-Dimensional and Tissue Doppler Echocardiographic Index for Diagnosing and Prognosticating Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction
Abstract
Introduction: The diagnosis of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) remains challenging. In this study, a novel echocardiography index based on three-dimensional and tissue Doppler echocardiography for diagnosing and estimating prognosis in HFpEF.
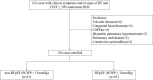
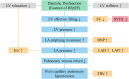
Materials and methods: Patients with symptoms and/or signs of heart failure and normal left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF ≥50%) who underwent right heart catheterization were screened. Patients were divided based on pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (PCWP) of ≥15 mmHg and PCWP <15 mmHg. A diagnosis of HFpEF was confirmed by PCWP of ≥15 mmHg according to ESC guidelines. A novel index was calculated by the ratio between stroke volume standardized to body surface area (SVI) and tissue Doppler mitral annulus systolic peak velocity S' (SVI/S'). Its diagnostic and prognostic values were determined.
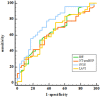
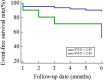
Results: A total of 104 patients (mean age 64 ± 12 years) were included. Of these, 63 had PCWP ≥15 mmHg and 41 patients had PCWP <15 mmHg. Compared to the PCWP <15 mmHg group, the ≥15 mmHg group had a significantly lower SVI/S' (P < 0.001). Logistic regression showed that SVI/S' was associated with high PCWP measured invasively. The SVI/S' had an area under the curve of 0.761 for diagnosing classifying between PCWP ≥15 mmHg and <15 mmHg. Kaplan-Meier analysis showed that the lower SVI/S' group showed a poorer prognosis.
Conclusions: SVI/S' is a non-invasive index calculated by three-dimensional and tissue Doppler echocardiography. It is a surrogate measure of PCWP and can be used to diagnose and determine prognosis in HFpEF.
Keywords: a novel echocardiography index; diagnosis; heart failure with preserved ejection fraction; prognosis; right heart catheterization.
Copyright © 2022 Wang, Mu, Liu, Xie, Zhang, Zhang, Che, Tse, Liu, Li and Fu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ponikowski P, Voors AA, Anker SD, Bueno H, Cleland J, Coats A, et al. . 2016 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: the Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Developed with the special contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur Heart J. (2016) 37:2129–200. 10.1093/eurheartj/ehw128 - DOI - PubMed
-
- De Marco M, Gerdts E, Mancusi C, Roman MJ, Lønnebakken MT, Lee ET, et al. . Influence of left ventricular stroke volume on incident heart failure in a population with preserved ejection fraction (from the strong heart study). Am J Cardiol. (2017) 119:1047–52. 10.1016/j.amjcard.2016.12.011 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hummel YM, Liu L, Lam C, Fonseca-Munoz DF, Damman K, Rienstra M, et al. . Echocardiographic estimation of left ventricular and pulmonary pressures in patients with heart failure and preserved ejection fraction: a study utilizing simultaneous echocardiography and invasive measurements. Eur J Heart Fail. (2017) 19:1651–60. 10.1002/ejhf.957 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

