Application Values of 2D and 3D Radiomics Models Based on CT Plain Scan in Differentiating Benign from Malignant Ovarian Tumors
- PMID: 35224097
- PMCID: PMC8872698
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/5952296
Application Values of 2D and 3D Radiomics Models Based on CT Plain Scan in Differentiating Benign from Malignant Ovarian Tumors
Abstract
Background: Accurate identification of ovarian tumors as benign or malignant is highly crucial. Radiomics is a new branch of imaging that has emerged in recent years to replace the traditional naked eye qualitative diagnosis.
Objective: This study is aimed at exploring the difference in the application potential of two- (2D) and three-dimensional (3D) radiomics models based on CT plain scan in differentiating benign from malignant ovarian tumors.
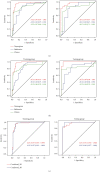
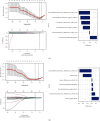
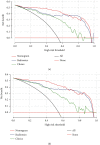
Method: A retrospective analysis was performed on 140 patients with ovarian tumors confirmed by surgery and pathology in our hospital from July 2017 to August 2020. These 140 patients were divided into benign group and malignant group according to the pathological results. The ITK-SNAP software was used to outline the regions-of-interest (ROI) of 2D or 3D tumors on the CT plain scan image of each patient; the texture features were extracted through analysis kit (AK), and the cases were randomly divided into training groups (n = 99) and validation group (n = 41) in a ratio of 7 : 3. The least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) algorithm was used to perform dimensionality reduction, followed by the construction of the radiomics nomogram model using the logistic regression method. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was drawn, and the calibration curve and decision curve analysis (DCA) were used to evaluate and verify the results of the radiomics nomogram and compare the differences between 2D and 3D diagnostic performance.
Results: There were 396 quantitative radiomics feature parameters extracted from 2D group and the 3D group, respectively. The area under the curve (AUC) of the radiomics nomogram of the 2D training group and the validation group were 0.96 and 0.97, respectively. The accuracy, specificity, and sensitivity of the training set were 92.9%, 88.9%, and 96.3%, respectively, and those of the validation set were 90.2%, 82.6%, and 100.0%, respectively. The AUCs of the radiomics nomogram of the 3D training group and validation group were 0.96% and 0.99%, respectively. The accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity of the training set were 92.9%, 96.3%, and 88.9%, respectively, and those of the validation set were 97.6%, 95.7%, and 100.0%, respectively. DeLong's test indicated that there was no statistical significance between the two sets (P > 0.05).
Conclusions: For the differential diagnosis of benign and malignant ovarian tumors, the 2D and 3D radiomics nomogram models exhibited comparable diagnostic performance. Considering that the 2D model was cost-effective and time-efficient, it was more recommended to use 2D features in future research.
Copyright © 2022 Shiyun Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A radiomics approach for automated diagnosis of ovarian neoplasm malignancy in computed tomography.Sci Rep. 2021 Apr 22;11(1):8730. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-87775-x. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33888749 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic value of a CT-based radiomics nomogram for discrimination of benign and early stage malignant ovarian tumors.Eur J Med Res. 2023 Dec 19;28(1):609. doi: 10.1186/s40001-023-01561-1. Eur J Med Res. 2023. PMID: 38115095 Free PMC article.
-
[Prediction of platinum-based chemotherapy sensitivity for epithelial ovarian cancer by multi-sequence MRI-based radiomic nomogram].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2022 Jan 18;102(3):201-208. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112137-20210816-01844. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35042289 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
Advancing personalised care in ovarian cancer using CT and MRI radiomics.Clin Radiol. 2025 May;84:106833. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2025.106833. Epub 2025 Jan 31. Clin Radiol. 2025. PMID: 40117992 Review.
-
Value of Assessment of Different Neoplasias in the Adnexa in the Differential Diagnosis of Malignant Ovarian Tumor and Benign Ovarian Tumor: A Meta-analysis.Ultrasound Med Biol. 2022 May;48(5):730-742. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2022.02.001. Epub 2022 Mar 7. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2022. PMID: 35272892 Review.
Cited by
-
Non-Invasive Prediction of Survival Time of Midline Glioma Patients Using Machine Learning on Multiparametric MRI Radiomics Features.Front Neurol. 2022 May 2;13:866274. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.866274. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35585843 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review and meta-analysis of CT and MRI radiomics in ovarian cancer: methodological issues and clinical utility.Insights Imaging. 2023 Jul 3;14(1):117. doi: 10.1186/s13244-023-01464-z. Insights Imaging. 2023. PMID: 37395888 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Performance of radiomics analysis in ultrasound imaging for differentiating benign from malignant adnexal masses: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2025 Aug;104(8):1433-1442. doi: 10.1111/aogs.15146. Epub 2025 May 1. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2025. PMID: 40312890 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of computer-aided diagnostics in the preoperative diagnosis of ovarian cancer: a systematic review.Insights Imaging. 2023 Feb 15;14(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s13244-022-01345-x. Insights Imaging. 2023. PMID: 36790570 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lack of incremental value of three-dimensional measurement in assessing invasiveness for lung cancer.Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2023 Dec 1;64(6):ezad373. doi: 10.1093/ejcts/ezad373. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2023. PMID: 37975876 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

