Emotion Regulation as a Pathway Connecting Early Life Adversity and Inflammation in Adulthood: a Conceptual Framework
- PMID: 35224511
- PMCID: PMC8863511
- DOI: 10.1007/s42844-022-00051-3
Emotion Regulation as a Pathway Connecting Early Life Adversity and Inflammation in Adulthood: a Conceptual Framework
Abstract
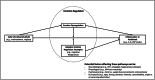
Chronic inflammation is implicated in a variety of diseases (e.g., cardiovascular disease and cancer). Much evidence suggests that early life adversity (ELA), such as maltreatment or neglect, can increase risk for inflammation in adulthood. ELA may program proinflammatory activity via its effects on brain areas involved in emotion regulation. Of multiple emotion regulation strategies, some are considered maladaptive (e.g., expressive suppression), while others are generally adaptive (e.g., cognitive reappraisal). We propose a conceptual framework for how emotion regulation tendencies may affect vulnerability or resilience to inflammation in adults who experienced adversity in childhood and/or adolescence. In support of this framework, we summarize evidence for the relationships between emotion dysregulation and higher inflammation (i.e., vulnerability), as well as between cognitive reappraisal and lower inflammation (i.e., resilience), in healthy adults with a history of ELA. Plausible neurobiological, physiological, psychosocial, and ELA-specific factors, as well as interventions, contributing to these associations are discussed. Strengths and limitations of the extant research, in addition to ideas for future directions, are presented.
Keywords: Cognitive reappraisal; Early life adversity; Emotion regulation; Inflammation; Resilience; Vulnerability.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Switzerland AG 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing InterestsThe authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Andersen E, Geiger P, Schiller C, Bluth K, Watkins L, Zhang Y, Xia K, Tauseef H, Leserman J, Girdler S, Gaylord S. Effects of Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction on experimental pain sensitivity and cortisol responses in women with early life abuse: A randomized controlled trial. Psychosomatic Medicine. 2021;83(6):515–527. doi: 10.1097/PSY.0000000000000889. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
