Human study on cancer diagnostic probe (CDP) for real-time excising of breast positive cavity side margins based on tracing hypoxia glycolysis; checking diagnostic accuracy in non-neoadjuvant cases
- PMID: 35224879
- PMCID: PMC8986141
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.4503
Human study on cancer diagnostic probe (CDP) for real-time excising of breast positive cavity side margins based on tracing hypoxia glycolysis; checking diagnostic accuracy in non-neoadjuvant cases
Abstract
Background: Cancer diagnostic probe (CDP) had been developed to detect involved breast cavity side margins in real-time (Miripour et al. Bioeng Transl Med. e10236.). Here, we presented the results of the in vivo human model CDP studies on non-neoadjuvant cases.
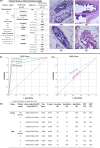
Methods: This study is a prospective, blind comparison to a gold standard, and the medical group recruited patients. CDP and frozen data were achieved before the permanent pathology experiment. The main outcome of the study is surgical margin status. From November 2018 to April 2020, 202 patients were registered, and 188 were assigned for the study. Breast-conserving surgery at any age or gender, re-surgery due to re-currency, or involved margins are acceptable. Patients must be non-neoadjuvant. The reliability of CDP scoring had been evaluated by the pathology of the scored IMs. Then, three models of the study were designed to compare CDP with the frozen sections. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves and AUC were measured based on the permanent postoperative pathology gold standard.
Results: A matched clinical diagnostic categorization between the pathological results of the tested IMs and response peaks of CDP on 113 cases, was reported (sensitivity = 97%, specificity = 89.3%, accuracy = 92%, positive predictive value (PPV) = 84.2%, and negative predictive value (NPV) = 98%). Study A showed the independent ability of CDP for IM scoring (sensitivity = 80%, specificity = 90%, accuracy = 90%, PPV = 22.2%, and NPV = 99.2%). Study B showed the complementary role of CDP to cover the missed lesions of frozen sections (sensitivity = 93.8%, specificity = 91%, accuracy = 91%, PPV = 55.6%, and NPV = 99.2%). Study C showed the ability of CDP in helping the pathologist to reduce his/her frozen miss judgment (specificity = 92%, accuracy = 93%, PPV = 42.1%, and NPV = 100%). Results were reported based on the post-surgical permanent pathology gold standard.
Conclusion: CDP scoring ability in intra-operative margin detection was verified on non-neoadjuvant breast cancer patients. Non-invasive real-time diagnosis of IMs with pathological values may make CDP a distinct tool with handheld equipment to increase the prognosis of breast cancer patients.
Keywords: cancer surgery; clinical study; hypoxia assisted glycolysis; pathology.
© 2022 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Four USA patents (One granted; US Patent US10,786,188 B1, and three publications; US Patent App. US2018/0299401 A1, US2021/0007638 A1, and US2021/0022650 A1) have been published based on this work. M.A. is a member of the scientific advisory board of Arya Nano biosensor Manufacturer Co., a company that is commercializing CDP technology. The remaining authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Clinical validation on role of cancer diagnostic probe in detecting the involved cavity margins missed in permanent pathology of tumor side in breast cancer surgery.Diagn Pathol. 2024 Nov 20;19(1):148. doi: 10.1186/s13000-024-01574-2. Diagn Pathol. 2024. PMID: 39568025 Free PMC article.
-
Accuracy of cancer diagnostic probe for intra-surgical checking of cavity side margins in neoadjuvant breast cancer cases: A human model study.Int J Med Robot. 2022 Feb;18(1):e2335. doi: 10.1002/rcs.2335. Epub 2021 Oct 5. Int J Med Robot. 2022. PMID: 34571582
-
Electrochemical tracing of hypoxia glycolysis by carbon nanotube sensors, a new hallmark for intraoperative detection of suspicious margins to breast neoplasia.Bioeng Transl Med. 2021 Jun 14;7(1):e10236. doi: 10.1002/btm2.10236. eCollection 2022 Jan. Bioeng Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 35079624 Free PMC article.
-
Intra-operative touch preparation cytology; does it have a role in re-excision lumpectomy?Ann Surg Oncol. 2007 Mar;14(3):1045-50. doi: 10.1245/s10434-006-9263-x. Epub 2007 Jan 6. Ann Surg Oncol. 2007. PMID: 17206481
-
Accuracy of frozen section in intraoperative margin assessment for breast-conserving surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2021 Mar 18;16(3):e0248768. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0248768. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33735315 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The presence of cancer-associated fibroblast in breast cavity side margins is in correlation with the expression of oncoproteins by adjacent epithelial cells: a new era in cancerous potential.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024 Sep 17;150(9):421. doi: 10.1007/s00432-024-05943-8. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39287633 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing breast cancer diagnosis through machine learning algorithms.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 2;15(1):23316. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-07628-9. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40603572 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical validation on role of cancer diagnostic probe in detecting the involved cavity margins missed in permanent pathology of tumor side in breast cancer surgery.Diagn Pathol. 2024 Nov 20;19(1):148. doi: 10.1186/s13000-024-01574-2. Diagn Pathol. 2024. PMID: 39568025 Free PMC article.
-
High-Frequency (30 MHz-6 GHz) Breast Tissue Characterization Stabilized by Suction Force for Intraoperative Tumor Margin Assessment.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Jan 4;13(2):179. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13020179. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36672989 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209‐249. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

