Relationship between optical coherence tomography angiography and visual evoked potential in patients with multiple sclerosis
- PMID: 35225535
- PMCID: PMC9114564
- DOI: 10.4103/ijo.IJO_431_21
Relationship between optical coherence tomography angiography and visual evoked potential in patients with multiple sclerosis
Abstract
Purpose: This study aimed to identify an easy-to-apply biomarker by correlating visual evoked potential (VEP) with optical coherence tomography angiography (OCTA) results in multiple sclerosis (MS).
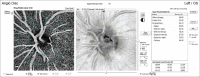
Methods: Our study was planned prospectively. Patients with MS were divided into two groups, VEP prolonged group 1 and VEP normal group 2. Age-matched and gender-matched healthy individuals (group 3) were included as the control group. Vascular density (VD) of the optic nerve head (ONH) and radial peripapillary capillaries (RPCs) were measured and recorded by OCTA. The optic nerve damage of patients was measured and recorded with a VEP device.
Results: Thirty-two eyes were included in group 1, 50 eyes were included in group 2, and 51 healthy eyes were included in group 3. In terms of visual acuity, group 1 was significantly lower than the other groups (P < 0.001). Regardless of the prolongation of p100 latency in patients with MS, whole image, inside disc ONH VD and in the same sectors in RPC VD were found to be significantly lower than the control group (P < 0.05). Retinal nerve fiber layer thickness was found to be significantly lower in group 1 than in group 2 and group 3 (P < 0.05). There was a significant correlation between low ONH VD and RPC VD and prolonged VEP P100 (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: VEP measurements can be correlated with OCTA measurements in patients with MS and can be used as a biomarker to determine the degree of optic nerve damage.
Keywords: Multiple sclerosis; optical coherence tomography angiography; visual evoked potential.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures

References
-
- Uher T, Vaneckova M, Sormani MP, Krasensky J, Sobisek L, Dusankova JB, et al. Identification of multiple sclerosis patients at highest risk of cognitive impairment using an integrated brain magnetic resonance imaging assessment approach. Eur J Neurol. 2017;24:292–301. - PubMed
-
- Hyun JW, Park G, Kwak K, Jo HJ, Joung A, Kim JH, et al. Deep gray matter atrophy in neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder and multiple sclerosis. Eur J Neurol. 2017;24:437–45. - PubMed
-
- Weiner HL. Multiple sclerosis is an inflammatory T-cell-mediated autoimmune disease. JAMA Neurol. 2004;61:1613–5. - PubMed
-
- Modrego PJ, Pina MA. Trends in prevalence and incidence of multiple sclerosis in Bajo Aragon, Spain. J Neurol Sci. 2003;216:89–93. - PubMed
-
- Lanzillo R, Cennamo G, Criscuolo C, Carotenuto A, Velotti N, Sparnelli F, et al. Optical coherence tomography angiography retinal vascular network assessment in multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler. 2018;24:1706–14. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

