The SUMOylation inhibitor subasumstat potentiates rituximab activity by IFN1-dependent macrophage and NK cell stimulation
- PMID: 35226739
- PMCID: PMC11022956
- DOI: 10.1182/blood.2021014267
The SUMOylation inhibitor subasumstat potentiates rituximab activity by IFN1-dependent macrophage and NK cell stimulation
Abstract
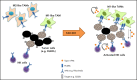
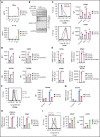
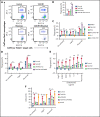
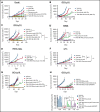
Small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) is a member of a ubiquitin-like protein superfamily. SUMOylation is a reversible posttranslational modification that has been implicated in the regulation of various cellular processes including inflammatory responses and expression of type 1 interferons (IFN1). In this report, we have explored the activity of the selective small molecule SUMOylation inhibitor subasumstat (TAK-981) in promoting antitumor innate immune responses. We demonstrate that treatment with TAK-981 results in IFN1-dependent macrophage and natural killer (NK) cell activation, promoting macrophage phagocytosis and NK cell cytotoxicity in ex vivo assays. Furthermore, pretreatment with TAK-981 enhanced macrophage phagocytosis or NK cell cytotoxicity against CD20+ target cells in combination with the anti-CD20 antibody rituximab. In vivo studies demonstrated enhanced antitumor activity of TAK-981 and rituximab in CD20+ lymphoma xenograft models. Combination of TAK-981 with anti-CD38 antibody daratumumab also resulted in enhanced antitumor activity. TAK-981 is currently being studied in phase 1 clinical trials (#NCT03648372, #NCT04074330, #NCT04776018, and #NCT04381650; www.clinicaltrials.gov) for the treatment of patients with lymphomas and solid tumors.
© 2022 by The American Society of Hematology.
Figures

Comment in
-
(SUMO)-wrestling with rituximab.Blood. 2022 May 5;139(18):2728-2730. doi: 10.1182/blood.2022015912. Blood. 2022. PMID: 35511190 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
A small-molecule SUMOylation inhibitor activates antitumor immune responses and potentiates immune therapies in preclinical models.Sci Transl Med. 2021 Sep 15;13(611):eaba7791. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aba7791. Epub 2021 Sep 15. Sci Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 34524860 Free PMC article.
-
Phase I/II Study of Subasumstat (TAK-981) in Combination With Rituximab in Relapsed/Refractory Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma.Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2025 May 3:S2152-2650(25)00151-X. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2025.04.020. Online ahead of print. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2025. PMID: 40467383
-
Asciminib stands out as the superior tyrosine kinase inhibitor to combine with anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies for the treatment of CD20+ Philadelphia-positive B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia in preclinical models.Haematologica. 2024 Nov 1;109(11):3520-3532. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2023.284853. Haematologica. 2024. PMID: 38841802 Free PMC article.
-
Rituximab: a review of its use in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukaemia.Drugs. 2003;63(8):803-43. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200363080-00005. Drugs. 2003. PMID: 12662126 Review.
-
SUMOylation and related post-translational modifications in natural killer cell anti-cancer responses.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 May 25;11:1213114. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1213114. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37313439 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting of SUMOylation leads to cBAF complex stabilization and disruption of the SS18::SSX transcriptome in Synovial Sarcoma.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2024 Jun 6:rs.3.rs-4362092. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-4362092/v1. Res Sq. 2024. PMID: 38883782 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Mechanisms and functions of SUMOylation in health and disease: a review focusing on immune cells.J Biomed Sci. 2024 Jan 27;31(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s12929-024-01003-y. J Biomed Sci. 2024. PMID: 38280996 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The PML hub: An emerging actor of leukemia therapies.J Exp Med. 2023 Aug 7;220(8):e20221213. doi: 10.1084/jem.20221213. Epub 2023 Jun 29. J Exp Med. 2023. PMID: 37382966 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted inhibition of SUMOylation: treatment of tumors.Hum Cell. 2024 Sep;37(5):1347-1354. doi: 10.1007/s13577-024-01092-9. Epub 2024 Jun 10. Hum Cell. 2024. PMID: 38856883 Review.
-
Predictive levels of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), thymidine kinase 1 (TK1) with interleukin-6 (IL-6), plasma T cells, NK cells as well as B cells in treating diffuse large B-cell lymphoma receiving rituximab.J Med Biochem. 2025 Jul 4;44(4):784-791. doi: 10.5937/jomb0-54911. J Med Biochem. 2025. PMID: 40837360 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Reff ME, Carner K, Chambers KS, et al. Depletion of B cells in vivo by a chimeric mouse human monoclonal antibody to CD20. Blood. 1994;83(2):435–445. - PubMed
-
- Cittera E, Leidi M, Buracchi C, et al. The CCL3 family of chemokines and innate immunity cooperate in vivo in the eradication of an established lymphoma xenograft by rituximab. J Immunol. 2007;178(10):6616–6623. - PubMed
-
- Dall'Ozzo S, Tartas S, Paintaud G, et al. Rituximab-dependent cytotoxicity by natural killer cells: influence of FCGR3A polymorphism on the concentration-effect relationship. Cancer Res. 2004;64(13):4664–4669. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

