The SUMOylation inhibitor subasumstat potentiates rituximab activity by IFN1-dependent macrophage and NK cell stimulation
- PMID: 35226739
- PMCID: PMC11022956
- DOI: 10.1182/blood.2021014267
The SUMOylation inhibitor subasumstat potentiates rituximab activity by IFN1-dependent macrophage and NK cell stimulation
Abstract
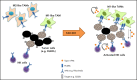
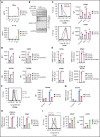
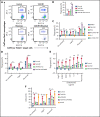
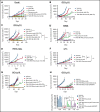
Small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) is a member of a ubiquitin-like protein superfamily. SUMOylation is a reversible posttranslational modification that has been implicated in the regulation of various cellular processes including inflammatory responses and expression of type 1 interferons (IFN1). In this report, we have explored the activity of the selective small molecule SUMOylation inhibitor subasumstat (TAK-981) in promoting antitumor innate immune responses. We demonstrate that treatment with TAK-981 results in IFN1-dependent macrophage and natural killer (NK) cell activation, promoting macrophage phagocytosis and NK cell cytotoxicity in ex vivo assays. Furthermore, pretreatment with TAK-981 enhanced macrophage phagocytosis or NK cell cytotoxicity against CD20+ target cells in combination with the anti-CD20 antibody rituximab. In vivo studies demonstrated enhanced antitumor activity of TAK-981 and rituximab in CD20+ lymphoma xenograft models. Combination of TAK-981 with anti-CD38 antibody daratumumab also resulted in enhanced antitumor activity. TAK-981 is currently being studied in phase 1 clinical trials (#NCT03648372, #NCT04074330, #NCT04776018, and #NCT04381650; www.clinicaltrials.gov) for the treatment of patients with lymphomas and solid tumors.
© 2022 by The American Society of Hematology.
Figures

Comment in
-
(SUMO)-wrestling with rituximab.Blood. 2022 May 5;139(18):2728-2730. doi: 10.1182/blood.2022015912. Blood. 2022. PMID: 35511190 No abstract available.
References
-
- Reff ME, Carner K, Chambers KS, et al. Depletion of B cells in vivo by a chimeric mouse human monoclonal antibody to CD20. Blood. 1994;83(2):435–445. - PubMed
-
- Cittera E, Leidi M, Buracchi C, et al. The CCL3 family of chemokines and innate immunity cooperate in vivo in the eradication of an established lymphoma xenograft by rituximab. J Immunol. 2007;178(10):6616–6623. - PubMed
-
- Dall'Ozzo S, Tartas S, Paintaud G, et al. Rituximab-dependent cytotoxicity by natural killer cells: influence of FCGR3A polymorphism on the concentration-effect relationship. Cancer Res. 2004;64(13):4664–4669. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

