Effect of a fixed-dose combination of Telmisartan/S-amlodipine on circadian blood pressure compared with Telmisartan monotherapy: TENUVA-BP study
- PMID: 35227313
- PMCID: PMC8886760
- DOI: 10.1186/s40885-021-00184-0
Effect of a fixed-dose combination of Telmisartan/S-amlodipine on circadian blood pressure compared with Telmisartan monotherapy: TENUVA-BP study
Abstract
Background: This study evaluated the circadian efficacy of a telmisartan 40 mg/S-amlodipine 2.5 mg fixed-dose combination (Telmisartan40/S-Amlodipine2.5) compared to telmisartan 80 mg (Telmisartan80) in patients with essential hypertension who did not respond to 2-4 weeks' treatment with telmisartan 40 mg.
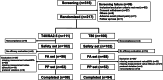
Methods: Eligible patients with essential hypertension (clinic mean sitting systolic blood pressure [MSSBP] ≥140 mmHg, or ≥ 130 mmHg in those with diabetes mellitus or chronic kidney disease) were randomly assigned to Telmisartan40/S-Amlodipine2.5 or Telmisartan80 for 8 weeks. All patients underwent ambulatory BP monitoring (ABPM) at baseline and 8 weeks later. Primary endpoints were changes in mean 24-h SBP and DBP on 24-h ABPM from baseline after 8 weeks. Secondary endpoints were changes in daytime, nighttime, and morning SBP and DBP, and clinic MSSBP and MSDBP.
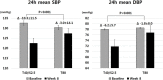
Results: A total of 316 Korean patients were enrolled, 217 patients were randomized to treatment, and 192 patients completed the study. Compared to Telmisartan80, Telmisartan40/S-Amlodipine2.5 showed significantly better reductions in 24-h mean SBP and DBP after 8 weeks. Telmisartan40/S-Amlodipine2.5 also significantly reduced secondary endpoints compared to Telmisartan80. Among 15 adverse events (7 [Telmisartan40/S-Amlodipine2.5] and 8 [Telmisartan80]), there were five adverse drug reactions; 14 events were mild, and none were identified with significant between-group differences.
Conclusions: Telmisartan40/S-Amlodipine2.5 was tolerable and more effective than Telmisartan80 in lowering 24-h mean ambulatory BP in patients with essential hypertension not responding adequately to Telmisartan40. Our findings support the fact that the combination of S-amlodipine with telmisartan is more appropriate than increasing the dose of telmisartan monotherapy.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov , NCT02231788 . Registered 4 September 2014.
Keywords: Amlodipine; Circadian rhythm; Drug combinations; Essential hypertension; Telmisartan.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest regarding the content of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Weber MA, Schiffrin EL, White WB, Mann S, Lindholm LH, Kenerson JG, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for the management of hypertension in the community: a statement by the American Society of Hypertension and the International Society of Hypertension. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich) 2014;16:14–26. doi: 10.1111/jch.12237. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Williams B, Mancia G, Spiering W, Agabiti Rosei E, Azizi M, Burnier M, Clement D, Coca A, de Simone G, Dominiczak A, Kahan T, Mahfoud F, Redon J, Ruilope L, Zanchetti A, Kerins M, Kjeldsen S, Kreutz R, Laurent S, Lip GYH, McManus R, Narkiewicz K, Ruschitzka F, Schmieder R, Shlyakhto E, Tsioufis K, Aboyans V, Desormais I. 2018 practice guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology and the European Society of Hypertension. Blood Press. 2018;27(6):314–340. doi: 10.1080/08037051.2018.1527177. - DOI - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
