E-series resolvin metabolome, biosynthesis and critical role of stereochemistry of specialized pro-resolving mediators (SPMs) in inflammation-resolution: Preparing SPMs for long COVID-19, human clinical trials, and targeted precision nutrition
- PMID: 35227568
- PMCID: PMC8847098
- DOI: 10.1016/j.smim.2022.101597
E-series resolvin metabolome, biosynthesis and critical role of stereochemistry of specialized pro-resolving mediators (SPMs) in inflammation-resolution: Preparing SPMs for long COVID-19, human clinical trials, and targeted precision nutrition
Abstract
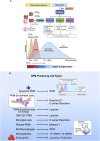
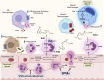
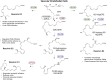
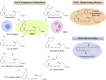
The COVID-19 pandemic has raised international awareness of the importance of rigorous scientific evidence and the havoc caused by uncontrolled excessive inflammation. Here we consider the evidence on whether the specialized pro-resolving mediators (SPMs) are ready to meet this challenge as well as targeted metabololipidomics of the resolution-inflammation metabolomes. Specific stereochemical mechanisms in the biosynthesis of SPMs from omega-3 essential fatty acids give rise to unique local-acting lipid mediators. SPMs possess stereochemically defined potent bioactive structures that are high-affinity ligands for cognate G protein-coupled surface receptors that evoke the cellular responses required for efficient resolution of acute inflammation. The SPMs biosynthesized from the major omega-3 fatty acids eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) are coined Resolvins (resolution phase interaction products; E series and D-series), Protectins and Maresins (macrophage mediators in resolving inflammation). Their biosynthesis and stereochemical assignments are established and confirmed (>1,441 resolvin publications in PubMed.gov) as well as their functional roles on innate immune cells and adaptive immune cells (both lymphocyte T-cell subsets and B-cells). The resolution of a protective acute inflammatory response is governed mainly by phagocytes that actively clear apoptotic cells, debris, blood clots and pathogens. These resolution phase functions of the acute inflammatory response are enhanced by SPMs, which together prepare the inflammatory loci for homeostasis and stimulate tissue regeneration via activating stem cells and the biosynthesis of novel cys-SPMs (e.g. MCTRs, PCTRs and RCTRs). These cys-SPMs also activate regeneration, are organ protective and stimulate resolution of local inflammation. Herein, we review the biosynthesis and functions of the E-series resolvins, namely resolvin E1 (the first n-3 resolvin identified), resolvin E2, resolvin E3 and resolvin E4 biosynthesized from their precursor eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and the critical role of total organic synthesis in confirming SPM complete stereochemistry, establishing their potent functions in resolution of inflammation, and novel structures. The physical properties of each biologically derived SPM, i.e., ultra-violet (UV) absorbance, chromatographic behavior, and tandem mass spectrometry (MS2) fragmentation, were matched to SPMs biosynthesized and prepared by stereospecific total organic synthesis. We briefly review this approach, also used with the endogenous D-series resolvins, protectins and maresins confirming their potent functions in resolution of inflammation, that paves the way for their rigorous evaluation in human tissues and clinical trials. The assignment of complete stereochemistry for each of the E and D series Resolvins, Protectins and Maresins was a critical and required step that enabled human clinical studies as in SPM profiling in COVID-19 infections and experimental animal disease models that also opened the promise of resolution physiology, resolution pharmacology and targeted precision nutrition as new areas for monitoring health and disease mechanisms.
Keywords: Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA); Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA); Human phagocytes; M2 macrophages; Neutrophils; Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Netea M.G., Balkwill F., Chonchol M., Cominelli F., Donath M.Y., Giamarellos-Bourboulis E.J., Golenbock D., Gresnigt M.S., Heneka M.T., Hoffman H.M., Hotchkiss R., Joosten L.A.B., Kastner D.L., Korte M., Latz E., Libby P., Mandrup-Poulsen T., Mantovani A., Mills K.H.G., Nowak K.L., O’Neill L.A., Pickkers P., van der Poll T., Ridker P.M., Schalkwijk J., Schwartz D.A., Siegmund B., Steer C.J., Tilg H., van der Meer J.W.M., van de Veerdonk F.L., Dinarello C.A. A guiding map for inflammation. Nat. Immunol. 2017;18(8):826–831. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Serhan C.N., Ward P.A., Gilroy D.W. Cambridge University Press; New York: 2010. Fundamentals of Inflammation.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

