Age-related differences in SARS-CoV-2 binding factors: An explanation for reduced susceptibility to severe COVID-19 among children?
- PMID: 35227628
- PMCID: PMC8823960
- DOI: 10.1016/j.prrv.2022.01.008
Age-related differences in SARS-CoV-2 binding factors: An explanation for reduced susceptibility to severe COVID-19 among children?
Abstract
Context: In contrast with other respiratory viruses, children infected with SARS-CoV-2 are largely spared from severe COVID-19.
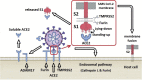
Objectives: To critically assess age-related differences in three host proteins involved in SARS-CoV-2 cellular entry: angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), transmembrane serine protease 2 (TMPRSS2) and furin.
Methods: We systematically searched Medline, Embase, and PubMed databases for relevant publications. Studies were eligible if they evaluated ACE2, TMPRSS2 or furin expression, methylation, or protein level in children.
Results: Sixteen papers were included. Age-dependent differences in membrane-bound and soluble ACE2 were shown in several studies, with ACE2 expression increasing with age. TMPRSS2 and furin are key proteases involved in SARS-CoV-2 spike protein cleavage. TMPRSS2 expression is increased by circulating androgens and is thus low in pre-pubertal children. Furin has not currently been well researched.
Limitations: High levels of study heterogeneity.
Conclusions: Low expression of key host proteins may partially explain the reduced incidence of severe COVID-19 among children, although further research is needed.
Keywords: ACE2; COVID-19; Furin; Paediatric; SARS-CoV-2; TMPRSS2.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard: World Health Organisation; 2021 [cited 12 September 2021]. Available from: https://covid19.who.int/.
-
- Castagnoli R., Votto M., Licari A., Brambilla I., Bruno R., Perlini S., et al. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection in children and adolescents: A systematic review. JAMA Pediatr. 2020;174(9):882–889. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous