Heterotopic Gastric Mucosa in Middle Esophagus Complicated with Esophageal Ulcers
- PMID: 35228416
- PMCID: PMC9556244
- DOI: 10.2169/internalmedicine.8705-21
Heterotopic Gastric Mucosa in Middle Esophagus Complicated with Esophageal Ulcers
Abstract
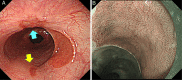
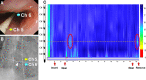
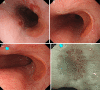
Heterotopic gastric mucosa (HGM) of esophagus, primarily occurring in cervical esophagus, is usually asymptomatic. A healthy woman (mid-40s) with postprandial heartburn was diagnosed with middle esophageal HGM and esophageal ulcers by esophagogastroduodenoscopy. Using 8-channel pH monitoring, a sensor near the HGM area detected postprandial acid phase (pH 3-4), while areas adjacent to the proximal and distal sensors were neutral, suggesting acid secretion from the HGM. A biopsy showed fundic gland tissue expressing H+/K+-ATPase and pepsinogen-I. Oral vonoprazan improved the clinical symptoms and endoscopic findings. This is the first report using 8-channel pH monitoring to diagnose extremely rare middle esophageal HGM.
Keywords: acid suppressive therapy; esophageal ulcer; heterotopic gastric mucosa; inlet patch; pH monitoring; potassium-competitive acid blocker.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Endoscopic diagnosis of cervical esophageal heterotopic gastric mucosa with conventional and narrow-band images.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Jan 7;20(1):242-9. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i1.242. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 24415878 Free PMC article.
-
Heterotopic gastric mucosa of the esophagus: literature-review and proposal of a clinicopathologic classification.Am J Gastroenterol. 2004 Mar;99(3):543-51. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2004.04082.x. Am J Gastroenterol. 2004. PMID: 15056100 Review.
-
Heterotopic Gastric Mucosa in the Distal Part of Esophagus in a Teenager: Case Report.Medicine (Baltimore). 2015 Oct;94(42):e1722. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000001722. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015. PMID: 26496283 Free PMC article.
-
Heterotopic gastric mucosa in the upper esophagus ("inlet patch"): a rare cause of esophageal perforation.Am J Gastroenterol. 1999 Oct;94(10):3047-50. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.1999.01458.x. Am J Gastroenterol. 1999. PMID: 10520868
-
Spontaneous perforation in the upper oesophagus resulting from ulcer in heterotopic gastric mucosa.Rev Laryngol Otol Rhinol (Bord). 2007;128(3):197-200. Rev Laryngol Otol Rhinol (Bord). 2007. PMID: 18323333 Review.
Cited by
-
Endoscopic submucosal dissection combined surgery for the treatment of ectopic gastric mucosa and ectopic pancreas in muscularis propria and serosal layer of the stomach: A rare case report and review of the literature.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Feb 28;104(9):e41297. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000041297. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40020126 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pediatric Heterotopic Gastric Mucosa of the Cervical Esophagus (Inlet Patch): Case Series with Clinical, Endoscopic, and Histopathological Correlation.Children (Basel). 2025 Jun 10;12(6):752. doi: 10.3390/children12060752. Children (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40564709 Free PMC article.
-
Nonpolypous Hamartomas of the Gastrointestinal Tract: An Updated Review on Classification, Denominations, and Clinical Management.J Oncol. 2022 May 9;2022:6983460. doi: 10.1155/2022/6983460. eCollection 2022. J Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35586207 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Risk Factors for Symptoms in Patients With Heterotopic Gastric Mucosa in the Upper Esophagus.Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2025 Jan 9;2025:7658517. doi: 10.1155/grp/7658517. eCollection 2025. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2025. PMID: 39823050 Free PMC article.
-
Gastric and Pancreatic Ectopic Mucosa in the Gallbladder: A Unique Mimicker of Polypoid Lesions.Cureus. 2024 Sep 11;16(9):e69231. doi: 10.7759/cureus.69231. eCollection 2024 Sep. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39268020 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Korkut E, Bektaş M, Alkan M, et al. . Esophageal motility and 24-h pH profiles of patients with heterotopic gastric mucosa in the cervical esophagus. Eur J Intern Med 21: 21-24, 2010. - PubMed
-
- Kohler B, Köhler G, Riemann JF. Spontaneous esophagotracheal fistula resulting from ulcer in heterotopic gastric mucosa. Gastroenterology 95: 828-830, 1988. - PubMed

