Ultrafast Dynamic Contrast-enhanced MRI of the Breast: How Is It Used?
- PMID: 35228489
- PMCID: PMC9199976
- DOI: 10.2463/mrms.rev.2021-0157
Ultrafast Dynamic Contrast-enhanced MRI of the Breast: How Is It Used?
Abstract
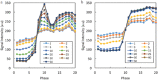
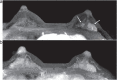
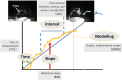
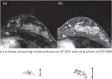
Ultrafast dynamic contrast-enhanced (UF-DCE) MRI is a new approach to capture kinetic information in the very early post-contrast period with high temporal resolution while keeping reasonable spatial resolution. The detailed timing and shape of the upslope in the time-intensity curve are analyzed. New kinetic parameters obtained from UF-DCE MRI are useful in differentiating malignant from benign lesions and in evaluating prognostic markers of the breast cancers. Clinically, UF-DCE MRI contributes in identifying hypervascular lesions when the background parenchymal enhancement (BPE) is marked on conventional dynamic MRI. This review starts with the technical aspect of accelerated acquisition. Practical aspects of UF-DCE MRI include identification of target hypervascular lesions from marked BPE and diagnosis of malignant and benign lesions based on new kinetic parameters derived from UF-DCE MRI: maximum slope (MS), time to enhance (TTE), bolus arrival time (BAT), time interval between arterial and venous visualization (AVI), and empirical mathematical model (EMM). The parameters derived from UF-DCE MRI are compared in terms of their diagnostic performance and association with prognostic markers. Pitfalls of UF-DCE MRI in the clinical situation are also covered. Since UF-DCE MRI is an evolving technique, future prospects of UF-DCE MRI are discussed in detail by citing recent evidence. The topic covers prediction of treatment response, multiparametric approach using DWI-derived parameters, evaluation of tumor-related vessels, and application of artificial intelligence for UF-DCE MRI. Along with comprehensive literature review, illustrative clinical cases are used to understand the value of UF-DCE MRI.
Keywords: breast; compressed sensing; dynamic contrast enhanced; magnetic resonance imaging; ultrafast.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest associated with this manuscript.
Figures






References
-
- Morris EA, Comstock CE, Lee CH. ACR BI-RADS® magnetic resonance imaging, In: ACR BI-RADS® atlas, breast imaging reporting and data system 2013. Reston:American College of Radiology, 2013; 15–18.
-
- Kuhl CK, Schrading S, Strobel K, Schild HH, Hilgers RD, Bieling HB. Abbreviated breast magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): first postcontrast subtracted images and maximum-intensity projection-a novel approach to breast cancer screening with MRI. J Clin Oncol 2014; 32:2304–2310.10.1200/JCO.2013.52.5386 - DOI - PubMed

