A noninvasive and comprehensive method for continuous assessment of cerebral blood flow pulsation based on magnetic induction phase shift
- PMID: 35228911
- PMCID: PMC8881914
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.13002
A noninvasive and comprehensive method for continuous assessment of cerebral blood flow pulsation based on magnetic induction phase shift
Abstract
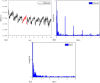
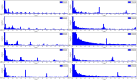
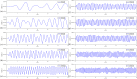
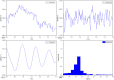
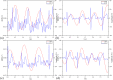
Cerebral blood flow (CBF) monitoring is of great significance for treating and preventing strokes. However, there has not been a fully accepted method targeting continuous assessment in clinical practice. In this work, we built a noninvasive continuous assessment system for cerebral blood flow pulsation (CBFP) that is based on magnetic induction phase shift (MIPS) technology and designed a physical model of the middle cerebral artery (MCA). Physical experiments were carried out through different simulations of CBF states. Four healthy volunteers were enrolled to perform the MIPS and ECG synchronously monitoring trials. Then, the components of MIPS related to the blood supply level and CBFP were investigated by signal analysis in time and frequency domain, wavelet decomposition and band-pass filtering. The results show that the time-domain baseline of MIPS increases with blood supply level. A pulse signal was identified in the spectrum (0.2-2 Hz in 200-2,000 ml/h groups, respectively) of MIPS when the simulated blood flow rate was not zero. The pulsation frequency with different simulated blood flow rates is the same as the squeezing frequency of the feeding pump. Similar to pulse waves, the MIPS signals on four healthy volunteers all had periodic change trends with obvious peaks and valleys. Its frequency is close to that of the ECG signal and there is a certain time delay between them. These results indicate that the CBFP component can effectively be extracted from MIPS, through which different blood supply levels can be distinguished. This method has the potential to become a new solution for non-invasive and comprehensive monitoring of CBFP.
Keywords: Cerebral blood flow; Magnetic induction phase shift; Noninvasive continuous assessment; Strokes.
© 2022 Zeng et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures








References
-
- Biesbroek JM, Niesten JM, Dankbaar JW, Biessels GJ, Velthuis BK, Reitsma JB, Van Der, Schaaf IC, Biesbroek JM, Niesten JM, Dankbaar JW, Biessels GJ, Velthuis BK, Reitsma JB, Van Der Schaaf IC. Diagnostic accuracy of CT perfusion imaging for detecting acute ischemic stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cerebrovascular Diseases. 2013;35(6):493–501. doi: 10.1159/000350200. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

