A Pain in the Neck: An Adolescent with Neck Pain
- PMID: 35229110
- PMCID: PMC8996527
- DOI: 10.1542/pir.2020-004168
A Pain in the Neck: An Adolescent with Neck Pain
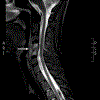
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

