Active and sham transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) improved quality of life in female patients with fibromyalgia
- PMID: 35229253
- PMCID: PMC9250466
- DOI: 10.1007/s11136-022-03106-1
Active and sham transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) improved quality of life in female patients with fibromyalgia
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Active and sham transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) improved quality of life in female patients with fibromyalgia.Qual Life Res. 2023 Oct;32(10):3001. doi: 10.1007/s11136-023-03478-y. Qual Life Res. 2023. PMID: 37488454 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
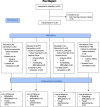
Purpose: Fibromyalgia (FM) is a chronic pain syndrome with a strong impact on quality of life (QoL). Treatment of this condition remains a challenge, due to the scarce evidence for the effectiveness of the therapeutic approaches available. Current attention is focused on transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS), which has yielded promising results for pain treatment. Rather than focusing only on pain relief, in this study, we aimed to determine how active or sham tDCS (over three cortical targets -the primary motor cortex, the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex and the operculo-insular cortex-) affect QoL in patients with FM.
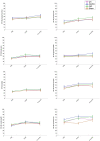
Methods: Using a double-blind, placebo-controlled design, we applied fifteen tDCS sessions of 20' to initial 130 participants (randomized to any of the four treatment groups). We evaluated the QoL (assessed by SF-36) and the symptoms' impact (assessed by FIQ-R) in baseline, after treatment and at 6 months follow-up.
Results: All groups were comparable as regards age, medication pattern and severity of symptoms before the treatment. We found that QoL and symptoms' impact improved in all treatment groups (including the sham) and this improvement lasted for up to 6 months. However, we did not observe any group effect nor group*treatment interaction.
Conclusions: After the intervention, we observed a non-specific effect that may be due to placebo, favoured by the expectations of tDCS efficacy and psychosocial variables inherent to the intervention (daily relationship with therapists and other patients in the clinic). Therefore, active tDCS is not superior to sham stimulation in improving QoL in FM.
Keywords: FIQ-R; Fibromyalgia; Quality of life (QoL); Randomized controlled trial (RCT); SF-36; Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS).
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors state that they do not have any competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Bartels EM, Dreyer L, Jacobsen S, Jespersen A, Bliddal H, Danneskiold-Samsøe B. Fibromyalgia, diagnosis and prevalence: Are gender differences explainable? Ugeskrift for Laeger. 2009;171(49):3588–3592. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

