GFPT2/GFAT2 and AMDHD2 act in tandem to control the hexosamine pathway
- PMID: 35229715
- PMCID: PMC8970586
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.69223
GFPT2/GFAT2 and AMDHD2 act in tandem to control the hexosamine pathway
Abstract
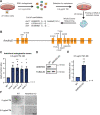
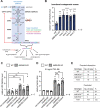
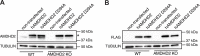
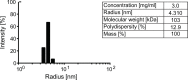
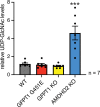
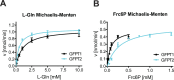
The hexosamine biosynthetic pathway (HBP) produces the essential metabolite UDP-GlcNAc and plays a key role in metabolism, health, and aging. The HBP is controlled by its rate-limiting enzyme glutamine fructose-6-phosphate amidotransferase (GFPT/GFAT) that is directly inhibited by UDP-GlcNAc in a feedback loop. HBP regulation by GFPT is well studied but other HBP regulators have remained obscure. Elevated UDP-GlcNAc levels counteract the glycosylation toxin tunicamycin (TM), and thus we screened for TM resistance in haploid mouse embryonic stem cells (mESCs) using random chemical mutagenesis to determine alternative HBP regulation. We identified the N-acetylglucosamine deacetylase AMDHD2 that catalyzes a reverse reaction in the HBP and its loss strongly elevated UDP-GlcNAc. To better understand AMDHD2, we solved the crystal structure and found that loss-of-function (LOF) is caused by protein destabilization or interference with its catalytic activity. Finally, we show that mESCs express AMDHD2 together with GFPT2 instead of the more common paralog GFPT1. Compared with GFPT1, GFPT2 had a much lower sensitivity to UDP-GlcNAc inhibition, explaining how AMDHD2 LOF resulted in HBP activation. This HBP configuration in which AMDHD2 serves to balance GFPT2 activity was also observed in other mESCs and, consistently, the GFPT2:GFPT1 ratio decreased with differentiation of human embryonic stem cells. Taken together, our data reveal a critical function of AMDHD2 in limiting UDP-GlcNAc production in cells that use GFPT2 for metabolite entry into the HBP.
Keywords: AMDHD2; biochemistry; chemical biology; genetics; genomics; gfat2; haploid mouse embryonic stem cells; hexosamine pathway; mouse; mutagenesis screen; x-ray crystallography.
© 2022, Kroef et al.
Conflict of interest statement
VK, SR, MH, KA, LE, SB, SM, UE, BS, UB, MD No competing interests declared
Figures














Similar articles
-
Cardiomyocyte protein O-GlcNAcylation is regulated by GFAT1 not GFAT2.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021 Dec 17;583:121-127. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.10.056. Epub 2021 Oct 29. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021. PMID: 34735873 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of GFAT-1 feedback regulation activates the hexosamine pathway that modulates protein homeostasis.Nat Commun. 2020 Feb 4;11(1):687. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-14524-5. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 32019926 Free PMC article.
-
Glutamine-fructose-6-phosphate transaminase 2 (GFPT2) promotes the EMT of serous ovarian cancer by activating the hexosamine biosynthetic pathway to increase the nuclear location of β-catenin.Pathol Res Pract. 2019 Dec;215(12):152681. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2019.152681. Epub 2019 Oct 3. Pathol Res Pract. 2019. PMID: 31685298
-
Hexosamines, insulin resistance, and the complications of diabetes: current status.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2006 Jan;290(1):E1-E8. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00329.2005. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2006. PMID: 16339923 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Hexosamine Biosynthesis Pathway: Regulation and Function.Genes (Basel). 2023 Apr 18;14(4):933. doi: 10.3390/genes14040933. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37107691 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Discovery of metal-binding proteins by thermal proteome profiling.Nat Chem Biol. 2024 Jun;20(6):770-778. doi: 10.1038/s41589-024-01563-y. Epub 2024 Feb 26. Nat Chem Biol. 2024. PMID: 38409364
-
Carbohydrate deacetylase, a key enzyme in oxidative chitin degradation, is evolutionarily linked to amino acid deacetylase.J Biol Chem. 2025 Apr;301(4):108420. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2025.108420. Epub 2025 Mar 18. J Biol Chem. 2025. PMID: 40113045 Free PMC article.
-
Functional characterisation of rare variants in genes encoding the MAPK/ERK signalling pathway identified in long-lived Leiden Longevity Study participants.Geroscience. 2025 May 29. doi: 10.1007/s11357-025-01699-2. Online ahead of print. Geroscience. 2025. PMID: 40442464
-
Sex-specific DNA methylation in saliva from the multi-ethnic Future of Families and Child Wellbeing Study.Epigenetics. 2023 Dec;18(1):2222244. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2023.2222244. Epigenetics. 2023. PMID: 37300819 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatics insights into the role of GFPT1 in breast invasive carcinoma: implications for tumor prognosis, immune modulation, and therapeutic applications.Front Genet. 2024 Nov 22;15:1482929. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1482929. eCollection 2024. Front Genet. 2024. PMID: 39664728 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams PD, Afonine PV, Bunkóczi G, Chen VB, Davis IW, Echols N, Headd JJ, Hung L-W, Kapral GJ, Grosse-Kunstleve RW, McCoy AJ, Moriarty NW, Oeffner R, Read RJ, Richardson DC, Richardson JS, Terwilliger TC, Zwart PH. PHENIX: a comprehensive Python-based system for macromolecular structure solution. Acta Crystallographica. Section D, Biological Crystallography. 2010;66:213–221. doi: 10.1107/S0907444909052925. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ahangar MS, Furze CM, Guy CS, Cooper C, Maskew KS, Graham B, Cameron AD, Fullam E. Structural and functional determination of homologs of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis N-acetylglucosamine-6-phosphate deacetylase (NagA) The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2018;293:9770–9783. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.002597. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

