Sero-reactivity to three distinct regions within the hepatitis C virus alternative reading frame protein (ARFP/core+1) in patients with chronic HCV genotype-3 infection
- PMID: 35230930
- PMCID: PMC9176264
- DOI: 10.1099/jgv.0.001727
Sero-reactivity to three distinct regions within the hepatitis C virus alternative reading frame protein (ARFP/core+1) in patients with chronic HCV genotype-3 infection
Abstract
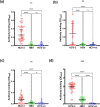
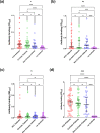
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection affects more than 71 million people worldwide. The disease slowly progresses to chronic, long-term liver injury which leads to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in 5 % of infections. The alternative reading frame protein (ARFP/core+1) is encoded by a sequence overlapping the HCV core gene in the +1 reading frame. Its role in hepatitis C pathogenesis and the viral life cycle is unclear, although some observers have related its production to disease progression and the development of HCC. The aim of this study was to determine whether ARFP is immunogenic in patients with chronic HCV genotype 3 infection and to assess whether sero-reactivity is associated with disease progression, particularly to HCC. Immunogenic epitopes within the protein were predicted by a bioinformatics tool, and three -20 aa length-peptides (ARFP-P1, ARFP-P2 and ARFP-P3) were synthesized and used in an avidin-biotin ARFP/core+1 peptide ELISA. Serum samples from 50 patients with chronic HCV genotype 3 infection, 50 genotype-1 patients, 50 HBV patients and 110 healthy controls were tested. Sero-reactivity to the ARFP peptides was also tested and compared in 114 chronic HCV genotype-3 patients subdivided on the basis of disease severity into non-cirrhotic, cirrhotic and HCC groups. Chronic HCV genotype-3 patients showed noticeable rates of reactivity to ARFP and core peptides. Seropositivity rates were 58% for ARFP-P1, 47 % for ARFP-P2, 5.9 % for ARFP-P3 and 100 % for C22 peptides. There was no significant difference between these seroreactivities between HCV genotype-3 patients with HCC, and HCV genotype-3 patients with and without liver cirrhosis. Patients with chronic HCV genotype-3 infection frequently produce antibodies against ARFP/core+1 protein. ARFP peptide reactivity was not associated with disease severity in patients with HCV genotype-3. These results support the conclusion that ARFP/core+1 is produced during HCV infection, but they do not confirm that antibodies to ARFP can indicate HCV disease progression.
Keywords: HCV genotype 3; alternative reading frame protein; disease progresssion; hepatitis C.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- de Moura MC. Non-A, non-B hepatitis: hepatitis C. Acta Med Port. 1990;3:209–212. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

