Modulation of RNA splicing associated with Wnt signaling pathway using FD-895 and pladienolide B
- PMID: 35230971
- PMCID: PMC8954975
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.203924
Modulation of RNA splicing associated with Wnt signaling pathway using FD-895 and pladienolide B
Abstract
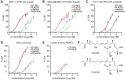
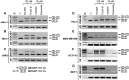
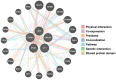
Alterations in RNA splicing are associated with different malignancies, including leukemia, lymphoma, and solid tumors. The RNA splicing modulators such as FD-895 and pladienolide B have been investigated in different malignancies to target/modulate spliceosome for therapeutic purpose. Different cell lines were screened using an RNA splicing modulator to test in vitro cytotoxicity and the ability to modulate RNA splicing capability via induction of intron retention (using RT-PCR and qPCR). The Cignal Finder Reporter Array evaluated [pathways affected by the splice modulators in HeLa cells. Further, the candidates associated with the pathways were validated at protein level using western blot assay, and gene-gene interaction studies were carried out using GeneMANIA. We show that FD-895 and pladienolide B induces higher apoptosis levels than conventional chemotherapy in different solid tumors. In addition, both agents modulate Wnt signaling pathways and mRNA splicing. Specifically, FD-895 and pladienolide B significantly downregulates Wnt signaling pathway-associated transcripts (GSK3β and LRP5) and both transcript and proteins including LEF1, CCND1, LRP6, and pLRP6 at the transcript, total protein, and protein phosphorylation's levels. These results indicate FD-895 and pladienolide B inhibit Wnt signaling by decreasing LRP6 phosphorylation and modulating mRNA splicing through induction of intron retention in solid tumors.
Keywords: FD-895; Wnt signaling; intron retention; pladienolide B; splice modulation; spliceosome; splicing.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

