Snapshots of nascent RNA reveal cell- and stimulus-specific responses to acute kidney injury
- PMID: 35230973
- PMCID: PMC8986083
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.146374
Snapshots of nascent RNA reveal cell- and stimulus-specific responses to acute kidney injury
Abstract
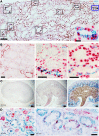
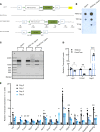
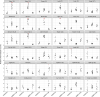
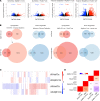
The current strategy to detect acute injury of kidney tubular cells relies on changes in serum levels of creatinine. Yet serum creatinine (sCr) is a marker of both functional and pathological processes and does not adequately assay tubular injury. In addition, sCr may require days to reach diagnostic thresholds, yet tubular cells respond with programs of damage and repair within minutes or hours. To detect acute responses to clinically relevant stimuli, we created mice expressing Rosa26-floxed-stop uracil phosphoribosyltransferase (Uprt) and inoculated 4-thiouracil (4-TU) to tag nascent RNA at selected time points. Cre-driven 4-TU-tagged RNA was isolated from intact kidneys and demonstrated that volume depletion and ischemia induced different genetic programs in collecting ducts and intercalated cells. Even lineage-related cell types expressed different genes in response to the 2 stressors. TU tagging also demonstrated the transient nature of the responses. Because we placed Uprt in the ubiquitously active Rosa26 locus, nascent RNAs from many cell types can be tagged in vivo and their roles interrogated under various conditions. In short, 4-TU labeling identifies stimulus-specific, cell-specific, and time-dependent acute responses that are otherwise difficult to detect with other technologies and are entirely obscured when sCr is the sole metric of kidney damage.
Keywords: Chronic kidney disease; Nephrology.
Figures


References
-
- Khwaja A. KDIGO clinical practice guidelines for acute kidney injury. Nephron Clin Pract. 2012;120(4):c179–c184. - PubMed
-
- Kellum JA, et al. Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) acute kidney injury work group. KDIGO clinical practice guideline for acute kidney injury. Kidney Int Suppl. 2012;2(1):1–138.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

