Small molecule LATS kinase inhibitors block the Hippo signaling pathway and promote cell growth under 3D culture conditions
- PMID: 35231442
- PMCID: PMC8988011
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.101779
Small molecule LATS kinase inhibitors block the Hippo signaling pathway and promote cell growth under 3D culture conditions
Abstract
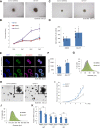
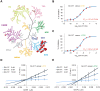
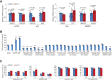
Although 3D cell culture models are considered to reflect the physiological microenvironment and exhibit high concordance with in vivo conditions, one disadvantage has been that cell proliferation is slower in 3D culture as compared to 2D culture. However, the signaling differences that lead to this slower proliferation are unclear. Here, we conducted a cell-based high-throughput screening study and identified novel small molecules that promote cell proliferation, particularly under 3D conditions. We found that one of these molecules, designated GA-017, increases the number and size of spheroids of various cell-types in both scaffold-based and scaffold-independent cultures. In addition, GA-017 also enhances the ex vivo formation of mouse intestinal organoids. Importantly, we demonstrate that GA-017 inhibits the serine/threonine protein kinases large tumor suppressor kinase 1/2, which phosphorylate Yes-associated protein and transcriptional coactivator with PDZ-binding motif , key effectors of the growth- and proliferation-regulating Hippo signaling pathway. We showed that GA-017 facilitates the growth of spheroids and organoids by stabilizing and translocating Yes-associated protein and transcriptional coactivator with PDZ-binding motif into the cell nucleus. Another chemical analog of GA-017 obtained in this screening also exhibited similar activities and functions. We conclude that experiments with these small molecule large tumor suppressor kinase inhibitors will contribute to further development of efficient 3D culture systems for the ex vivo expansion of spheroids and organoids.
Keywords: Hippo pathway; LATS; cell culture; high-throughput screening; inhibitor.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest All authors are inventors on patents related to this work. The authors declare that they have no other conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

