The use of high resolution optical coherence tomography (HR-OCT) in the diagnosis of ocular surface masqueraders
- PMID: 35231640
- PMCID: PMC9058205
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtos.2022.02.003
The use of high resolution optical coherence tomography (HR-OCT) in the diagnosis of ocular surface masqueraders
Abstract
Introduction: Ocular surface masqueraders encompass any ocular surface lesion masquerading as another ocular surface lesion. High resolution optical coherence tomography (HR-OCT) has emerged as an adjunctive tool to clinical acumen. This study's purpose is to evaluate the utility of HR-OCT images in guiding the diagnosis and management of those lesions.
Material and methods: 22 individuals with a clinically ambiguous ocular surface lesion with slit lamp photographs (SLP), HR-OCT images, and histopathological examination were included in the study. The presumptive clinical diagnosis based on SLP was compared to the diagnosis suggested by HR-OCT findings and to definitive diagnosis by histopathology. The main outcome of this study was the frequency in which HR-OCT findings guided the clinician to the correct diagnosis.
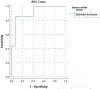
Results: 7 lesions were epithelial, 3 had an epithelial and a subepithelial component, and 12 were subepithelial. HR-OCT was most effective in discerning lesion location, successfully identifying the location in 100% of cases. Classic HR-OCT findings were detected in 68.2% of cases while suggestive features were detected in 31.8% of cases. The epithelial lesions' mean epithelial thickness was 265.4 ± 140.6 μm, the subepithelial lesions' mean was 58.0 ± 25.0 μm, and the combined lesions' mean was 140.0 ± 70.0 μm. The epithelium was significantly thicker in epithelial lesions compared to subepithelial and combined lesions. By ROC analysis we identified that using a cut off of 156 μm, the sensitivity was 86% and the specificity was 93%.
Discussion: HR-OCT can be a valuable diagnostic tool, assisting in the differentiation of ambiguous ocular surface pathologies by providing a cross-sectional, morphological image of the lesion.
Keywords: Amyloid; Classic; Epithelial; HR-OCT; Lymphoma; Masquerade; Melanoma; Ocular surface; Ocular surface squamous neoplasia; Squamous cell carcinoma; Subepithelial.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
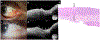

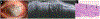
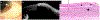


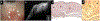
Similar articles
-
Diagnosis of ocular surface lesions using ultra-high-resolution optical coherence tomography.Ophthalmology. 2013 May;120(5):883-91. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2012.10.025. Epub 2013 Jan 21. Ophthalmology. 2013. PMID: 23347984 Free PMC article.
-
Ultra high-resolution anterior segment optical coherence tomography in the diagnosis and management of ocular surface squamous neoplasia.Ocul Surf. 2014 Jan;12(1):46-58. doi: 10.1016/j.jtos.2013.11.001. Epub 2013 Nov 9. Ocul Surf. 2014. PMID: 24439046 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spectrum of AS-OCT features of ocular surface tumors and correlation of clinico-tomographic features with histopathology: a study of 70 lesions.Int Ophthalmol. 2021 Nov;41(11):3571-3586. doi: 10.1007/s10792-021-01939-2. Epub 2021 Jul 9. Int Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 34241759
-
High-Resolution Optical Coherence Tomography as an Adjunctive Tool in the Diagnosis of Corneal and Conjunctival Pathology.Ocul Surf. 2015 Jul;13(3):226-35. doi: 10.1016/j.jtos.2015.02.001. Epub 2015 Apr 6. Ocul Surf. 2015. PMID: 26045235 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ultra-high resolution optical coherence tomography for differentiation of ocular surface squamous neoplasia and pterygia.Ophthalmology. 2012 Mar;119(3):481-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2011.08.028. Epub 2011 Dec 9. Ophthalmology. 2012. PMID: 22154538
Cited by
-
Ocular and inflammatory markers associated with Gulf War illness symptoms.Sci Rep. 2023 Mar 2;13(1):3512. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-30544-9. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36864130 Free PMC article.
-
Anterior segment optical coherence tomography in conjunctival ocular surface disorders - A review.Indian J Ophthalmol. 2025 Apr 1;73(4):543-552. doi: 10.4103/IJO.IJO_68_25. Epub 2025 Mar 27. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 40146141 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential diagnostic importance of swept-source optical coherence tomography in ocular surface lesions : Swept-source OCT in ocular surface lesions.BMC Ophthalmol. 2025 May 22;25(1):307. doi: 10.1186/s12886-025-04137-1. BMC Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 40405099 Free PMC article.
-
It Is All About the Angle: A Clinical and Optical Coherence Tomography Comparison of Corneal Ocular Surface Squamous Neoplasia and Corneal Pannus.Cornea. 2024 Oct 1;43(10):1249-1256. doi: 10.1097/ICO.0000000000003407. Epub 2023 Oct 26. Cornea. 2024. PMID: 37889526
References
-
- Theodore FH. Conjunctival carcinoma masquerading as chronic conjunctivitis. Eye Ear Nose Throat Mon. 1967;46:1419–20. - PubMed
-
- Shields CL, Alset AE, Boal NS, Casey MG, Knapp AN, Sugarman JA, et al. Conjunctival Tumors in 5002 Cases. Comparative Analysis of Benign Versus Malignant Counterparts. The 2016 James D. Allen Lecture. American Journal of Ophthalmology. 2017;173:106–33. - PubMed
-
- Sharma M, Sundar D, Vanathi M, Meel R, Kashyap S, Chawla R, et al. Invasive Ocular Surface Squamous Neoplasia Masquerading as Nodular Scleritis. Ophthalmic Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2017;33:e45–e7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

